@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository
v6.1.0
Published
The goal of SAP CAP CDS-QL BaseRepository is to significantly reduce the boilerplate code required to implement data access layers for persistance entities by providing out of the box actions on the database like .create(), .createMany(), .getAll(), .upda
Maintainers
Readme












The goal of BaseRepository is to significantly reduce the boilerplate code required to implement data access layers for persistance entities by providing out of the box actions on the database.
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Installation
- Usage
Option 1: UsingBaseRepositorywithStandard SAP CAP CDS-TSOption 2: UsingBaseRepositorywithCDS-TS-DispatcherDrafts:BaseRepositoryDraftMethodsHelpersDecorators
Samples- Contributing
- License
- Authors
Installation
Install CDS-TS-Repository
npm install @dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository[!IMPORTANT] CDS-TS-Repository uses
@sap/cds,@sap/cds-dkversion 9If you're using
@sap/cds,@sap/cds-dkversion 8then installnpm install @dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository@5.
Generate CDS Typed entities
Execute the following commands :
cds add typernpm install[!TIP] If above option is being used, this means whenever we change a
.CDSfile the changes will be reflected in the generated@cds-modelsfolder.
Important
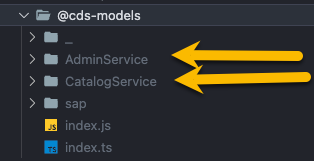
[!CAUTION] Import always the
generated entitiesfrom theservicefolders and not from theindex.ts
[!TIP] By default cds-typer will create in your
package.jsona quick path alias like :"imports": { "#cds-models/*": "./@cds-models/*/index.js" }Use import helper to import entities from
#cds-modelslike example :
import { Book } from '#cds-models/CatalogService';
Usage
Option 1 : Using BaseRepository with Standard SAP CAP CDS-TS
This guide explains how to use the BaseRepository with the Standard SAP CDS-TS, allowing you to work without the need for the CDS-TS-Dispatcher.
Step 1 : Create MyRepository class
Start by creating MyRepository class, which will extend the BaseRepository<T> to handle operations for your entity.
Example
import { BaseRepository, Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository'
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE'
// Imported to have visibility over INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE ...
import { Service } from '@sap/cds';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity)
}
public aMethod(req: Request<MyEntity>) {
const result1 = await this.create(...)
const result2 = await this.createMany(...)
const result5 = await this.getAll()
const result6 = await this.paginate(...)
const result7 = await this.find(...)
const result8 = await this.findOne(...)
const result9 = await this.delete(...)
const result10 = await this.update(...)
const result11 = await this.updateLocaleTexts(...)
const result12 = await this.exists(...)
const result13 = await this.count()
}
public anotherMethod(results: MyEntity[], req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}
// Enhance with custom QL methods ...
public customQLMethod() {
const customQL = SELECT(MyEntity).columns(...).where(...)
// ...
}
}
Step 2 : Integrate MyRepository class
Now that you have MyRepository class, you can integrate it into your implementation.
- Create a new private field:
private myRepository: MyRepository = new MyRepository();- Use the handler on the
callbackof theevents:
this.before('READ', MyEntity, (req) => this.myRepository.aMethod(req));
this.after('READ', MyEntity, (results, req) => this.myRepository.anotherMethod(results, req));Example
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MainService extends cds.ApplicationService {
private myRepository: MyRepository = new MyRepository();
init() {
this.before('READ', MyEntity, (req) => this.myRepository.aMethod(req));
this.after('READ', MyEntity, (results, req) => this.myRepository.anotherMethod(results, req));
return super.init();
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
Option 2 : Using BaseRepository with CDS-TS-Dispatcher
This guide explains how to use the BaseRepository with the CDS-TS-Dispatcher.
Step 1 : Create MyRepository class
Start by creating a MyRepository class, which will extend the BaseRepository<T> to handle operations for your entity.
- Create a new class
MyRepository:
export class MyRepository {}- Add
@Repositorydecorator :
@Repository()
export class MyRepository {}- Extend
MyRepositoryclass to inherit theBaseRepositorymethods
@Repository()
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // CDS-Typer entity
}
}Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository'
import { Repository, Service } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher'
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE'
@Repository()
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity) // CDS-Typer entity
}
aMethod() {
const result1 = await this.create(...)
const result2 = await this.createMany(...)
const result5 = await this.getAll()
const result6 = await this.paginate(...)
const result7 = await this.find(...)
const result8 = await this.findOne(...)
const result9 = await this.delete(...)
const result10 = await this.update(...)
const result11 = await this.updateLocaleTexts(...)
const result12 = await this.exists(...)
const result13 = await this.count()
}
// Enhance with custom QL methods ...
customQLMethod() {
const customQL = SELECT(MyEntity).columns(...).where(...)
// ...
}
}Step 2 : Inject MyRepository class
Now MyRepository class can be injected in another class using @Inject decorator.
Example
@EntityHandler(Book)
class MyEntityHandler {
@Inject(MyRepository) private readonly myRepository: MyRepository;
...
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
Drafts : BaseRepositoryDraft
The BaseRepositoryDraft class extends BaseRepository by providing support for draft-enabled entities.
The BaseRepositoryDraft repository provides a clear separation of methods for working with active entities and draft instances.
Use BaseRepository methods when dealing with active entity instances.
updatedeletecreatecreateMany...
Use BaseRepositoryDraft methods when working with draft entity instances.
updateDraftdeleteDraftfindOneDraftfindDrafts...
Usage
Example 1: Integrate BaseRepository & BaseRepositoryDraft using Mixin
import { BaseRepository, BaseRepositoryDraft, Mixin } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends Mixin(BaseRepository<MyEntity>, BaseRepositoryDraft<MyEntity>) {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity);
}
// ... define custom CDS-QL actions if BaseRepository ones are not satisfying your needs !
}[!NOTE] MyRepository class will inherit all methods for active entities and drafts.
Active entity methods: .create, createMany, update, exists, delete, deleteMany ...
Draft entity methods: .updateDraft, existsDraft, deleteDraft, deleteManyDrafts ...
Example 2: Use only BaseRepositoryDraft methods
import { BaseRepository, BaseRepositoryDraft, Mixin } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepositoryDraft<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity);
}
// ... define custom CDS-QL actions if BaseRepository ones are not satisfying your needs !
}[!IMPORTANT] Entity
MyEntitymust be annotated with@odata.draft.enabled: trueto useBaseRepositoryDraftmethods.
Methods
create
(method) this.create(entry: Entry<T>) : Promise<boolean>.
The create method allows you to create a new entry in the table.
Parameters
entry (object): An object representing the entry to be created. The object should match the structure expected byMyEntity
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise that resolves when the insertion operation is completed successfully.
Example 1
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const createdInstance = await this.create({
name: 'Customer 1',
description: 'Customer 1 description',
});
// Further logic with createdInstance
}
}Example 2
The method is also able to create deep entities like
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const createdInstance = > await this.create({
name: 'Customer 1',
description: 'Customer 1 description',
to_children: [{
name: 'child 1'
// ...
}]
});
// Further logic with createdInstance
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
createMany
(method) this.createMany(...entries: Entries<T>[]) : Promise<boolean>.
The createMany method allows you to add multiple entries in the table.
Parameters
entries (...entries: Entries<T>[]): An array of objects representing the entries to be created. Each object should match the structure expected byMyEntity.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns aPromisethat resolves when the insertion operation is completed successfully.
Example 1
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const create: MyEntity = {
name: 'Customer 1',
description: 'Customer 1 description',
},
{
name: 'Customer 2',
description: 'Customer 2 description',
};
// example 1
const createdInstance = await this.createMany([create]);
// example 2
const createdInstance2 = await this.createMany({
name: 'Customer 1',
description: 'Customer 1 description',
},
{
name: 'Customer 2',
description: 'Customer 2 description',
});
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
getAll
(method) this.getAll(): Promise<T[] | undefined>
The getAll method retrieves all table entries.
Return
Promise<T[] | undefined>: A Promise resolving to an array of typeT(e.g.,MyEntity). If no results are found, the Promise resolves toundefined.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
// Variant 1
const results = await this.getAll();
if (results) {
// do something with results
}
// Variant 2
const items = results?.length;
const oneItem = results![0];
// Further logic with results
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
getDistinctColumns
(method) this.getDistinctColumns<Column extends keyof T>(columns: Column[]>): Promise<Array<Pick<T, Column>> | undefined>
The getDistinctColumns method retrieves distinct values for the specified columns from the table.
Parameters
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of column names to retrieve distinct records for. Each column name should be of a type that matches the entity's schema.
Return
Promise<Array<Pick<T, Column>> | undefined>: A Promise resolving to an array of objects containing the selected columns from the entity. If no results are found, the Promise resolves toundefined.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const results = await this.getDistinctColumns(['currency_code', 'ID', 'name']);
// or using spread strings
// const results = await this.getDistinctColumns('currency_code', 'ID', 'name');
// Variant 1
if (results) {
// do something with results
}
// Variant 2
const items = results?.length;
const oneItem = results![0];
// Further logic with results
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
getLocaleTexts
(method) this.getLocaleTexts<Column extends keyof T>(columns: Column[]): Promise<Array<Pick<T, Column> & Locale> | undefined>
The getLocaleTexts method is designed to retrieve a list of items with localized text.
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of name of the columns to extract the localized text.
Return
Promise<Array<Pick<T, Column> & Locale> | undefined>: A Promise resolving to an array of objects containing the selected columns from the entity along with locale information. If no results are found, the Promise resolves toundefined.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const results = await this.getLocaleTexts(['descr', 'ID']);
// or
const results = await this.getLocaleTexts('descr', 'ID');
// Variant 1
if (results) {
// do something with results
}
// Variant 2
const items = results?.length;
const oneItem = results![0];
// Further logic with results
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
paginate
(method) this.paginate(options: { limit: number; skip?: number | undefined }): Promise<T[]>
The paginate method allows you to find and retrieve a list of items with optional pagination similar to limit from SQL.
Parameters
options(object): An object containing the following properties:limit(number): The maximum number of items to retrieve.skip?(optional, number): This property, if applied, will 'skip' a certain number of items (default: 0).
Return
Promise<T[] | undefined>: A Promise resolving to an array of objects representing instances of typeT(e.g.,MyEntity). If no results are found, the Promise resolves toundefined.
Example 1 : Retrieve the first 10 items
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const results = await this.paginate({ limit: 10 });
// Variant 1
if (results) {
// do something with results
}
// Variant 2
const items = results?.length;
const oneItem = results![0];
// Further logic with results
}
}Example 2 : Retrieve items starting from the 20th item, limit to 5 items
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const resultsWithSkip = await this.paginate({ limit: 5, skip: 20 });
// Variant 1
if (resultsWithSkip) {
// do something with results
}
// Variant 2
const items = resultsWithSkip?.length;
const oneItem = resultsWithSkip![0];
// Further logic with resultsWithSkip
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
find
The find method allows you to find and retrieve entries from the table that match the specified keys.
Overloads
| Method | Parameters | Description |
| :------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :---------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| this.find(): Promise<T | undefined> | | Get all table items. |
| this.find(keys: Entry<T>): Promise<T | undefined> | keys (object) | An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in MyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria. |
| this.find(filter :Filter<T>): Promise<T | undefined> | filter (Filter) | An instance of Filter<T> |
Return
Promise<T[] | undefined>: A Promise that resolves to an array of typeT(e.g.,MyEntity). If no results are found, the Promise resolves toundefined.
Example 1 using object
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const results = await this.find({ name: 'Customer', description: 'description' });
// Variant 1
if (results) {
// do something with results
}
// Variant 2
const items = results?.length;
const oneItem = results![0];
// Further logic with results
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
Example 2 using Filter
import { BaseRepository, Filter } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const filter = new Filter<MyEntity>({
field: 'name',
operator: 'LIKE',
value: 'Customer',
});
// Execute the query using the find
const results = await this.find(filter);
}
}[!TIP] See Filter for more complex QUERY filters
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
findOne
findOne(keys: Entry<T>): Promise<T | undefined>
The findOne method allows you to find and retrieve a single entry from the table that matches the specified keys.
Parameters
keys (object): An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in theMyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria.
Return
Promise<T | undefined>: This method returns a Promise with a single entry of typeT, whereTisMyEntity. If no result is found, the Promise resolves toundefined.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const itemFound = await this.findOne({ name: 'Customer', description: 'description' });
// Variant 1
if (itemFound) {
// do something with result
}
// Further logic with result
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
findOneAndUpdate
findOneAndUpdate(keys: Entry<T>, fieldsToUpdate: Entry<T>): Promise<boolean>
The findOneAndUpdate method performs an atomic find-and-update operation. It first checks if an entity matching the specified keys exists, and if found, updates it with the provided fields.
Parameters
keys (object): An object representing the keys to identify the entity to find. Each key should correspond to a property inMyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria.fieldsToUpdate (object): An object representing the fields and their new values to update on the found entity.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise that resolves to:trueif the entity was found and successfully updatedfalseif the entity was not found or the update failed
Example 1: Basic usage
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const wasUpdated = await this.findOneAndUpdate(
{ ID: '123' },
{ name: 'Updated Name', status: 'active' }
);
if (wasUpdated) {
console.log('Entity updated successfully');
} else {
console.log('Entity not found or update failed');
}
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the class.
[!TIP] The method first verifies entity existence before attempting the update, ensuring safe update operations.
builder
.find
Overloads
| Method | Parameters | Description |
| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :---------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| this.builder().find(): FindBuilder<T> | | Get all table items. |
| this.builder().find(keys: Entry<T>): FindBuilder<T> | keys (object) | An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in MyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria. |
| this.builder().find(filter :Filter<T>): FindBuilder<T> | filter (Filter) | An instance of Filter<T> |
Return
FindBuilder<T>: AFindBuilderinstance that provides access to the following methods for constructing aSELECT:
elements
Provides the Metadata of Entity fields.
Example
const results = this.builder().find().columns('ID', 'currency_code').elements;[!WARNING] Currently SAP does not offer typing on the
elements.
distinct
Skip duplicates similar to SQL distinct.
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find() // get all items
.distinct.columns('country')
.execute();orderAsc
To order the ASC selected columns, you can use the orderAsc methods. Pass an array of column names to specify the order.
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of name of the columns to order by.
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.orderAsc('name', 'ID', 'company')
// or
//.orderAsc(['name', 'ID', 'company'])
.execute();orderDesc
To order the DESC selected columns, you can use the orderDesc methods. Pass an array of column names to specify the order.
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of name of the columns to order by.
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.orderDesc('name', 'ID', 'company')
// or
//.orderDesc(['name', 'ID', 'company'])
.execute();paginate
This method allows retrieve a list of items with optional pagination similar to limit from SQL.
Parameters
options(object): An object containing the following properties:limit(number): The maximum number of items to retrieve.skip?(number): This property, if applied, will 'skip' a certain number of items (default: 0).
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.paginate({ limit: 1 })
.execute();groupBy
If you want to group the selected columns, use the groupBy method. Pass an array of column names to group by.
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of name of the columns to group by.
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.groupBy('name', 'company')
// or
//.groupBy(['name', 'company'])
.execute();columns
Specifies which columns to be fetched.
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of name of the columns to show only.
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.columns('name', 'currency_code')
// or
//.columns(['name', 'currency_code'])
.execute();[!WARNING] If
columns()method is used together withgetExpand()/columnsFormatter()/groupBy()/orderAsc()/orderDesc(), thecolumns()method can have impact on the final typing
columnsFormatter
The columnsFormatter can be used :
- To
renamecolumns in your query results. - To apply
aggregate functionsto specific columns, such as calculating averages, sums etc.
Parameters
columns (object-1, object-n, ...)column(string): The name of the column to be processed.column1(string): The name of the column to be processed. (Applied only forCONCAT)column2(string): The name of the column to be processed. (Applied only forCONCAT)aggregate?[optional] (string): This property, if applied, willcall aggregate functionfor the specifiedcolumnname, below you can find the available aggregate functions :- String :
'LOWER' | 'UPPER' | 'LENGTH' | 'CONCAT' | 'TRIM' - Number :
'AVG' | 'MIN' | 'MAX' | 'SUM' | 'ABS' | 'CEILING' | 'TOTAL' | 'COUNT' | 'ROUND' | 'FLOOR' - Date :
'DAY' | 'MONTH' | 'YEAR' | 'HOUR' | 'MINUTE' | 'SECOND'
- String :
renameAs(string): This property creates a new column with the given name
Example 1
const results = await this.builder()
.find()
.columnsFormatter(
{ column: 'price', aggregate: 'AVG', renameAs: 'average' },
{ column: 'stock', renameAs: 'stockRenamed' },
)
.execute();Example 2
const results = this.builder()
.find({ ID: 201 })
.getExpand(['reviews'])
.columns('reviews', 'bookName', 'authorName')
.columnsFormatter({ column1: 'bookName', column2: 'authorName', aggregate: 'CONCAT', renameAs: 'bookAndAuthorName' })
.execute();
// above typing will have the following properties
// 'reviews', 'bookName', 'authorName', 'bookAndAuthorName'getExpand
Use getExpand to specify which columns you want to expand from the table.
Overloads
| Type | Method | Parameters | Description |
| :-------------- | :---------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| Single expand | getExpand(...associations : Columns<T>[]): FindBuilder<T> | ...associations: Array<string> | Use Single expand when you want to expand only certain associations from the root level of the entity. -------- An array of strings representing the columns to expand, this will expand only first level of associations. |
| Deep expand | getExpand(associations : Expand<T>): FindBuilder<T> | associations: object | Use Deep expand option when you want to deep expand certain associations. -------- An object representing the columns to expand. Value: - {} - If empty object is used as a value for an association, the empty object will perform a full expand of the association. Properties: - select? : Array<string> [optional]: Fetch only the mentioned columns. - expand? : object [optional]: Expand nested associations. |
| Auto expand | getExpand(options : { levels : number }): FindBuilder<T> | levels: number | Use Auto expand to deep expand all associations within your entity. -------- You can control how deeply the method should expand associations by providing the levels. |
Example 1 : Auto expand
Root- Entitychild- (association) - expandedchild- (composition) - expanded- ...
child- (association) - expandedchild(association) - expanded- ...
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand({ levels: 2 })
.execute();Example 2 : Deep expand
// expand 'author', 'genre' and 'reviews' associations
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand({
// expand 'author'
author: {},
// expand 'genre', having only 'ID' and 'name'
genre: {
select: ['ID', 'name'],
},
// expand 'reviews', having only 'ID', 'book_ID' fields and 'reviewer' association
reviews: {
select: ['ID', 'book_ID'],
// expand 'reviewer', having only the 'ID'
expand: {
reviewer: {
select: ['ID'],
},
},
},
})
.execute();Example 3 : Deep expand stored in a variable & using columns()
import { Expand } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
// expand 'author', and 'reviews' associations
const associations: Expand<MyEntity> = {
// expand 'author'
author: {},
// expand 'reviews' having all fields + expand reviewer association having only 'ID'
reviews: {
// expand 'reviewer', having only the 'ID'
expand: {
reviewer: {
select: ['ID'],
},
},
},
};
const results = await this.builder()
.find() // get all items
.columns('author', 'reviews')
.getExpand(associations)
.execute();[!NOTE] If
columnsis used withgetExpandthecolumnsmethod will have impact on the final typing.
Example 4 : Simple expand (root only)
// expand only 'orders' and 'reviews' associations
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand('orders', 'reviews')
// or
//.getExpand(['orders', 'reviews'])
.execute();forUpdate
Exclusively locks the selected rows for subsequent updates in the current transaction, thereby preventing concurrent updates by other parallel transactions.
Parameters
options(object): An object containing the following properties:wait?(number) [optional]: an integer specifying the timeout after which to fail with an error in case a lock couldn't be obtained.
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand('orders', 'reviews')
.forUpdate({ wait: 5 })
//or
//.forUpdate()
.execute();[!TIP] More info can be found on the official SAP CAP forUpdate documentation.
forShareLock
Locks the selected rows in the current transaction, thereby preventing concurrent updates by other parallel transactions, until the transaction is committed or rolled back. Using a shared lock allows all transactions to read the locked record.
If a queried record is already exclusively locked by another transaction, the .forShareLock() method waits for the lock to be released.
Example
// Expand only 'orders' association
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand('orders', 'reviews')
.forShareLock()
.execute();[!TIP] More info can be found on the official SAP CAP forShareLock documentation. documentation.
hints
Passes hints to the database query optimizer that can influence the execution plan. The hints can be passed as individual arguments or as an array.
The SQL Optimizer usually determines the access path (for example, index search versus table scan) on the basis of the costs (Cost-Based Optimizer). You can override the SQL Optimizer choice by explicitly specifying hints in the query that enforces a certain access path.
Parameters
...hints(string[]): Query optimizer hings
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.hints('IGNORE_PLAN_CACHE', 'MAX_CONCURRENCY(1)')
.execute();[!IMPORTANT] This works only for
HANA DB.
[!TIP] More info can be found on the official SAP CAP hints documentation. documentation.
execute
Finally, to execute the constructed query and retrieve the results as an array of objects, use the execute method. It returns a promise that resolves to the constructed query result.
Return
Promise<T[] | undefined>: This method returns a Promise ofT[]orundefinedif nothing was found.
Example 1
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.execute();Example 2
const results = await this.builder()
.find({ name: 'A company name' })
.orderAsc(['name'])
.paginate({ limit: 5 })
.getExpand('orders')
.execute();[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
.findOne
Overloads
| Method | Parameters | Description |
| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :---------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| this.builder().findOne(keys: Entry<T>): FindOneBuilder<T> | keys (object) | An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in MyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria. |
| this.builder().findOne(filter :Filter<T>): FindOneBuilder<T> | filter (Filter) | An instance of Filter<T> |
Return
FindOneBuilder<T>: AFindOneBuilderinstance that provides access to the following methods for constructing aSELECT:
elements
Provides the Metadata of Entity fields.
Example
const oneResult = this.builder().findOne({ currency_code: 'USD' }).columns('ID', 'currency_code').elements;[!WARNING] Currently SAP does not offer typing on the
elements.
columns
Specifies which columns to be fetched.
Parameters
columns (...columns : Columns<T>[]): An array of name of the columns to show only.
Example
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.columns('name', 'currency_code')
// or
//.columns(['name', 'currency_code'])
.execute();[!WARNING] If
columns()method is used together withgetExpand()/columnsFormatter()thecolumns()method can have impact on the final typing
columnsFormatter
The columnsFormatter can be used :
- To
renamecolumns in your query results. - To apply
aggregate functionsto specific columns, such as calculating averages, sums etc.
Parameters
columns (object-1, object-n, ...)column(string): The name of the column to be processed.column1(string): The name of the column to be processed. (Applied only forCONCAT)column2(string): The name of the column to be processed. (Applied only forCONCAT)aggregate?[optional] (string): This property, if applied, willcall aggregate functionfor the specifiedcolumnname, below you can find the available aggregate functions :- String :
'LOWER' | 'UPPER' | 'LENGTH' | 'CONCAT' | 'TRIM' - ~~Number :
'AVG' | 'MIN' | 'MAX' | 'SUM' | 'ABS' | 'CEILING' | 'TOTAL' | 'COUNT' | 'ROUND' | 'FLOOR'.~~ Applicable only for this.builder().find - Date :
'DAY' | 'MONTH' | 'YEAR' | 'HOUR' | 'MINUTE' | 'SECOND'
- String :
renameAs(string): This property creates a new column with the given name
Example 1
const oneResult = this.builder()
.findOne({ ID: 201 })
.getExpand(['reviews'])
.columns('reviews', 'bookName', 'authorName')
.columnsFormatter({ column1: 'bookName', column2: 'authorName', aggregate: 'CONCAT', renameAs: 'bookAndAuthorName' })
.execute();
// above typing will have the following properties
// 'reviews', 'bookName', 'authorName', 'bookAndAuthorName'getExpand
Use getExpand to specify which columns you want to expand from the table.
Overloads
| Type | Method | Parameters | Description |
| :-------------- | :---------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| Single expand | getExpand(...associations : Columns<T>[]): FindBuilder<T> | ...associations: Array<string> | Use Single expand when you want to expand only certain associations from the root level of the entity. -------- An array of strings representing the columns to expand, this will expand only first level of associations. |
| Deep expand | getExpand(associations : Expand<T>): FindBuilder<T> | associations: object | Use Deep expand option when you want to deep expand certain associations. -------- An object representing the columns to expand. Value: - {} - If empty object is used as a value for an association, the empty object will perform a full expand of the association. Properties: - select? : Array<string> [optional]: Fetch only the mentioned columns. - expand? : object [optional]: Expand nested associations. |
| Auto expand | getExpand(options : { levels : number }): FindBuilder<T> | levels: number | Use Auto expand to deep expand all associations within your entity. -------- You can control how deeply the method should expand associations by providing the levels. |
Example 1 : Auto expand
Root- Entitychild- (association) - expandedchild- (composition) - expanded- ...
child- (association) - expandedchild(association) - expanded- ...
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand({ levels: 2 })
.execute();Example 2 : Deep expand
// expand 'author', 'genre' and 'reviews' associations
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand({
// expand 'author'
author: {},
// expand 'genre', having only 'ID' and 'name'
genre: {
select: ['ID', 'name'],
},
// expand 'reviews', having only 'ID', 'book_ID' fields and 'reviewer' association
reviews: {
select: ['ID', 'book_ID'],
// expand 'reviewer', having only the 'ID'
expand: {
reviewer: {
select: ['ID'],
},
},
},
})
.execute();Example 3 : Deep expand stored in a variable & using columns()
import { Expand } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
// expand 'author', and 'reviews' associations
const associations: Expand<MyEntity> = {
// expand 'author'
author: {},
// expand 'reviews' having all fields + expand reviewer association having only 'ID'
reviews: {
// expand 'reviewer', having only the 'ID'
expand: {
reviewer: {
select: ['ID'],
},
},
},
};
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.columns('author', 'reviews')
.getExpand(associations)
.execute();[!NOTE] If
columnsis used withgetExpandthecolumnsmethod will have impact on the final typing.
Example 4 : Simple expand
// expand only 'orders' and 'reviews' associations
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.getExpand('orders', 'reviews')
// or
//.getExpand(['orders', 'reviews'])
.execute();forUpdate
Exclusively locks the selected rows for subsequent updates in the current transaction, thereby preventing concurrent updates by other parallel transactions.
Parameters
options(object): An object containing the following properties:wait?(number) [optional]: an integer specifying the timeout after which to fail with an error in case a lock couldn't be obtained.
Example
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.forUpdate({ wait: 5 })
//or
//.forUpdate()
.execute();[!TIP] More info can be found on the official SAP CAP forUpdate documentation.
forShareLock
Locks the selected rows in the current transaction, thereby preventing concurrent updates by other parallel transactions, until the transaction is committed or rolled back. Using a shared lock allows all transactions to read the locked record.
If a queried record is already exclusively locked by another transaction, the .forShareLock() method waits for the lock to be released.
Example
// Expand only 'orders' association
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.forShareLock()
.execute();[!TIP] More info can be found on the official SAP CAP forShareLock documentation. documentation.
hints
Passes hints to the database query optimizer that can influence the execution plan. The hints can be passed as individual arguments or as an array.
The SQL Optimizer usually determines the access path (for example, index search versus table scan) on the basis of the costs (Cost-Based Optimizer). You can override the SQL Optimizer choice by explicitly specifying hints in the query that enforces a certain access path.
Parameters
...hints(string[]): Query optimizer hings
Example
const results = await this.builder()
.find({
name: 'A company name',
})
.hints('IGNORE_PLAN_CACHE', 'MAX_CONCURRENCY(1)')
.execute();[!IMPORTANT] This works only for
HANA DB
[!TIP] More info can be found on the official SAP CAP hints documentation. documentation.
execute
Finally, to execute the constructed query and retrieve the result as a single object, use the execute method. It returns a promise that resolves to the constructed query result.
Return
Promise<T | undefined>: This method returns a Promise ofTorundefinedif nothing was found.
Example 1
const oneResult = await this.builder()
.findOne({
name: 'A company name',
})
.execute();Example 2
const oneResult = await this.builder().findOne({ name: 'A company name' }).getExpand('orders').execute();[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
update
update(keys: Entry<T>, fieldsToUpdate: Entry<T>): Promise<boolean>
The update method allows you to update entries in the table that match the specified keys with new values for specific fields.
Parameters
keys (object): An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in theMyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria.fieldsToUpdate (object): An object representing the fields and their updated values for the matching entries.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif the update operation issuccessful, andfalseotherwise.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const updated = await this.update(
{ ID: 'a51ab5c8-f366-460f-8f28-0eda2e41d6db' },
{ name: 'a new name', description: 'a new description' },
);
// Further logic with updated
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
updateOrCreate
updateOrCreate(...entries: Entries<T>[]): Promise<boolean>
The updateOrCreate method is a database operation that will update an existing row if a specified value already exists in a table, and insert a new row if the specified value doesn't already exist, similar to UPSERT from SQL.
Parameters
entries (...entries: Entries<T>[]): An array of objects representing the entries to be created. Each object should match the structure expected byMyEntity.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif the update/create operation issuccessful, andfalseotherwise.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const updatedOrCreated = await bookRepository.updateOrCreate(
{
ID: 123,
title: 'Magic Forest',
descr: 'A magical journey through enchanted woods!',
},
{
ID: 456,
title: 'Mystic Mountain',
descr: 'Explore the mysteries of the ancient mountain!',
},
);
// Further logic with updated
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
updateLocaleTexts
updateLocaleTexts(localeCodeKeys: Entry<T> & Locale, fieldsToUpdate: Entry<T>): Promise<boolean>
The updateLocaleTexts method allows you to update entries in the table that match the specified localeCodeKeys with new values for specific fields.
Parameters
localeCodeKeys (object): An object containing language codes'en', 'de', 'fr', 'ro', ...and entity keys to filter entries.fieldsToUpdate (object): An object representing the keys and values to update. Each key corresponds to a property in the entity.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif the update operation issuccessful, andfalseotherwise.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const updated = await this.updateLocaleTexts({ locale: 'de', ID: 201 }, { name: 'ein neuer Name' });
// Further logic with updated
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
delete
delete(keys: Entry<T>): Promise<boolean>
The delete method allows you to delete entries from the table that match the specified keys.
Parameters
keys (object): An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in theMyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif the delete operation issuccessful, andfalseotherwise.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const deleted1 = await this.delete({ name: 'Customer' });
const deleted2 = await this.delete({ ID: '2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a02ba19' });
// Further logic with deleted1 and deleted2
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
deleteMany
deleteMany(...entries: Entries<T>[]): Promise<boolean>
The deleteMany method allows you to delete multiple entries from the table that match the specified keys.
Parameters
entries (...entries: Entries<T>[])- An object representing the keys to filter the entries. Each key should correspond to a property in theMyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif all instances were successfully deleted andfalseotherwise.
Example 1
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
// as an array of objects
const deleted = await this.deleteMany([
{ ID: '2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a02ba19' },
{ ID: 'a51ab5c8-f366-460f-8f28-0eda2e41d6db' },
]);
// as an spread of objects
const deleted2 = await this.deleteMany(
{ ID: '2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a02ba19' },
{ ID: 'a51ab5c8-f366-460f-8f28-0eda2e41d6db' },
);
// Further logic with deleted
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
deleteAll
deleteAll(): Promise<boolean>
The deleteAll method allows you to delete all entries from the table but preserving the table structure, performing a cleanup of the table.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif all instances were successfully deleted andfalseotherwise.
Example 1
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const deleted = await this.deleteAll();
// Further logic with deleted
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
exists
exists(keys: Entry<T>): Promise<boolean>
The exists method allows you to check whether entries exist in the table that match the specified fields.
Parameters
keys (object): Each key should correspond to a property in theMyEntity, and the values should match the filter criteria.
Return
Promise<boolean>: This method returns a Promise oftrueif the item exists in the databse andfalseotherwise.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const exists = await this.exists({ ID: '2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a02ba09' });
// Further logic with exists
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
count
count(): Promise<number>
The count method allows you to count all items from the table.
Return
Promise<number>: This method returns the count / number of items fromMyEntity.
Example
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'LOCATION_OF_YOUR_ENTITY_TYPE';
export class MyRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity); // a CDS Typer entity type
}
public async aMethod() {
const numberOfItemsInMyEntity = await this.count();
// Further logic with numberOfItemsInMyEntity
}
}[!NOTE] MyEntity



