@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp
v1.7.0
Published
MCP server for Chrome DevTools with WebMCP integration for connecting to website MCP tools
Maintainers
Readme
@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp
MCP server for Chrome DevTools - Let Claude, Cursor, Copilot, and Gemini control and debug Chrome browser
📖 WebMCP Documentation | 🚀 Quick Start | 🔌 Connecting Agents | 🎯 Chrome DevTools Quickstart
@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp lets AI coding agents like Claude, Gemini, Cursor, and Copilot control and inspect a live Chrome browser via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Get performance insights, debug network requests, take screenshots, and interact with website-specific MCP tools through WebMCP integration.
Note: This is a fork of ChromeDevTools/chrome-devtools-mcp published under the
@mcp-bscope. It includes WebMCP integration for connecting to MCP tools registered on webpages. The original project is developed by Google LLC and the ChromeDevTools team. See NOTICE for attribution details.
Why Use @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp?
| Feature | Benefit |
|---------|---------|
| 27 MCP Tools | Comprehensive browser control - navigation, input, screenshots, performance, debugging |
| WebMCP Integration | Connect to website-specific AI tools via @mcp-b/global |
| Performance Analysis | Chrome DevTools-powered performance insights and trace recording |
| Reliable Automation | Puppeteer-based with automatic waiting for action results |
| Works with All MCP Clients | Claude, Cursor, Copilot, Gemini CLI, VS Code, Windsurf, and more |
Token Efficiency
WebMCP tools are dramatically more efficient than screenshot-based workflows:
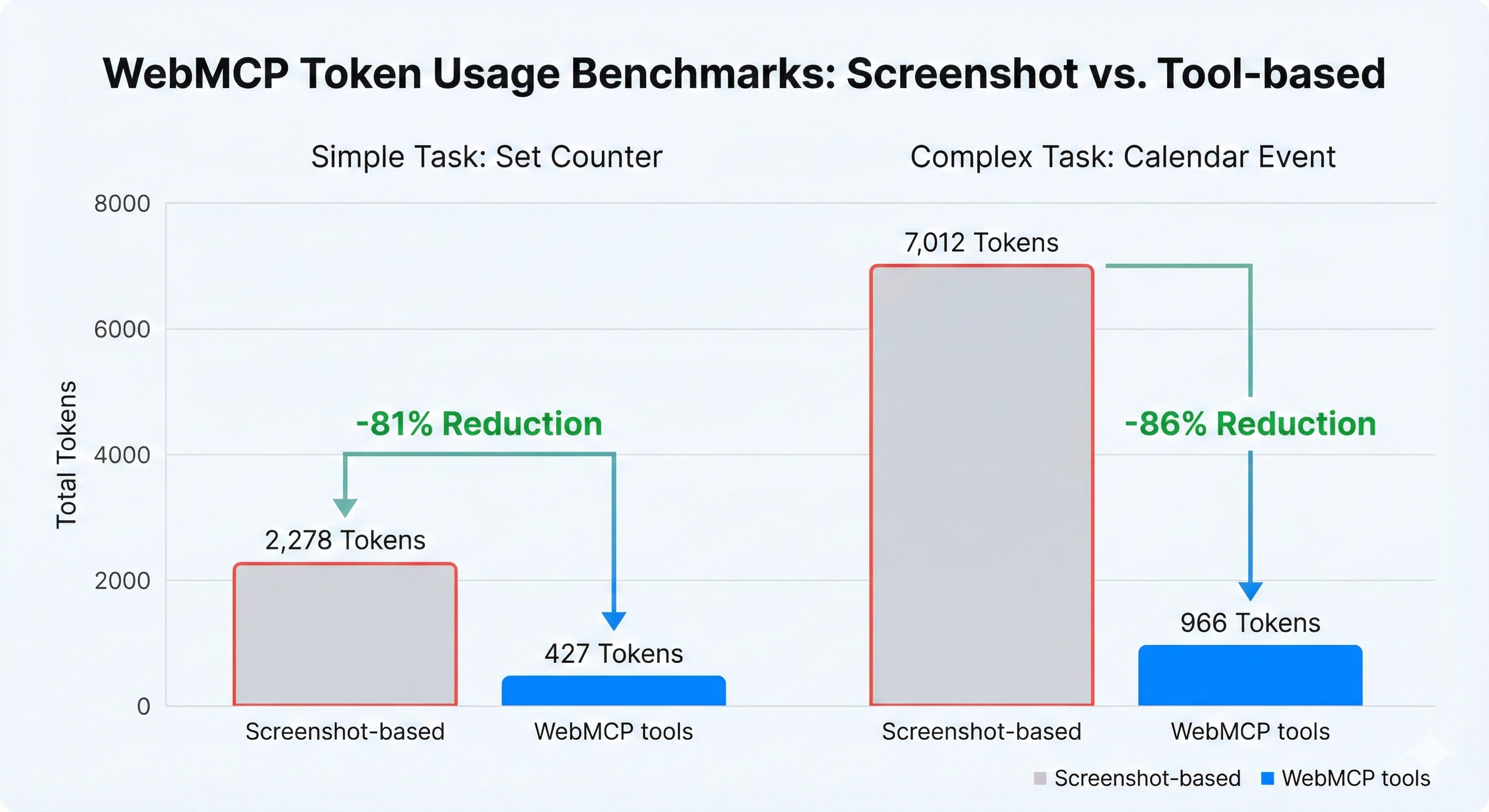
| Task | Screenshot-Based | WebMCP Tools | Savings | |------|-----------------|--------------|---------| | Simple task (set counter) | 3,801 tokens | 433 tokens | 89% fewer tokens | | Complex task (calendar event) | 11,390 tokens | 2,583 tokens | 77% fewer tokens |
Screenshots are expensive (~2,000 tokens each). WebMCP tool responses are compact JSON (20-100 tokens typically).
Try it yourself: Clone the Chrome DevTools Quickstart and run the benchmarks.
What's Different from Chrome DevTools MCP?
This fork adds WebMCP integration - the ability to call MCP tools that are registered directly on webpages. This unlocks a powerful new workflow:
| Feature | Chrome DevTools MCP | @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp | |---------|--------------------|-----------------------------| | Browser automation | ✅ | ✅ | | Performance analysis | ✅ | ✅ | | Network inspection | ✅ | ✅ | | Screenshot/snapshot | ✅ | ✅ | | Call website MCP tools | ❌ | ✅ | | List website MCP tools | ❌ | ✅ | | AI-driven tool development | ❌ | ✅ |
The key addition is automatic WebMCP tool discovery and registration. When you visit a page with @mcp-b/global, its tools are automatically registered as first-class MCP tools that your AI agent can call directly.
AI-Driven Development Workflow
One of the most powerful use cases for this package is AI-driven tool development - essentially test-driven development for AI agents. Here's how it works:
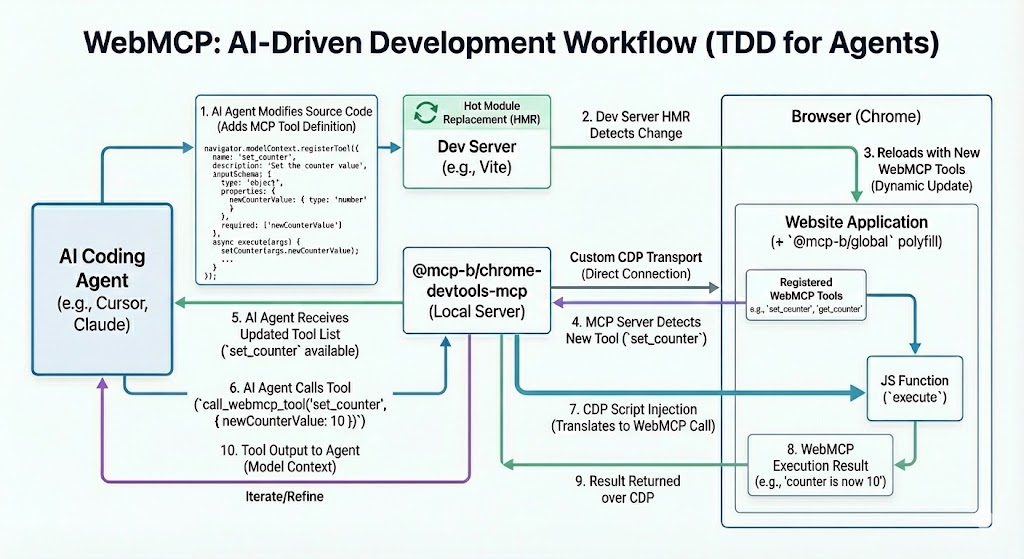
Want to try it yourself? Check out the Chrome DevTools Quickstart - a minimal example you can clone and run in 3 steps.
Example: Building a Search Tool
Imagine you're building a web app and want to add a search feature exposed as an MCP tool:
Step 1: Ask your AI agent to create the tool
Create a WebMCP tool called "search_products" that searches our product catalogStep 2: The AI writes the code in your app
// Your AI agent writes this code
import '@mcp-b/global';
navigator.modelContext.registerTool({
name: 'search_products',
description: 'Search for products by name or category',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
query: { type: 'string' },
category: { type: 'string' }
},
required: ['query']
},
async execute({ query, category }) {
const results = await searchProducts(query, category);
return {
content: [{ type: 'text', text: JSON.stringify(results) }]
};
}
});Step 3: Your dev server hot-reloads
Step 4: The AI tests it via Chrome DevTools MCP
Navigate to http://localhost:3000 and list the available toolsThe AI sees the new search_products tool appear.
Step 5: The AI calls the tool to verify it works
Use the search_products tool to search for "headphones"Step 6: If something is wrong, the AI iterates
The AI can see the actual response, fix any bugs, and repeat until it works perfectly.
Why This Matters
This creates a tight feedback loop where your AI assistant can:
- Write WebMCP tools in your codebase
- Deploy them automatically via hot-reload
- Discover them through
list_webmcp_tools - Test them by calling tools directly by their prefixed names (e.g.,
webmcp_localhost_3000_page0_search_products) - Debug issues using console messages and snapshots
- Iterate until the tool works correctly
This is like TDD for AI - the AI can build and verify its own tools in real-time.
Demo: Tool Execution Result
Here's what it looks like when an AI agent successfully discovers and calls WebMCP tools:

Tool reference | Changelog | Contributing | Troubleshooting | Design Principles
Key features
- Get performance insights: Uses Chrome DevTools to record traces and extract actionable performance insights.
- Advanced browser debugging: Analyze network requests, take screenshots and check the browser console.
- Reliable automation. Uses puppeteer to automate actions in Chrome and automatically wait for action results.
- WebMCP integration: Connect to MCP tools registered on webpages via @mcp-b/global, enabling AI agents to use website-specific functionality.
Disclaimers
@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp exposes content of the browser instance to the MCP clients
allowing them to inspect, debug, and modify any data in the browser or DevTools.
Avoid sharing sensitive or personal information that you don't want to share with
MCP clients.
Requirements
- Node.js v20.19 or a newer latest maintenance LTS version.
- Chrome current stable version or newer.
- npm.
Getting started
New to WebMCP? Try the Chrome DevTools Quickstart - clone, run, and see AI-driven tool development in action in under 5 minutes.
Add the following config to your MCP client:
{
"mcpServers": {
"chrome-devtools": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}[!NOTE] Using
@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestensures that your MCP client will always use the latest version of this Chrome DevTools MCP server with WebMCP integration.
MCP Client configuration
amp mcp add chrome-devtools -- npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestTo use the Chrome DevTools MCP server follow the instructions from Antigravity's docs to install a custom MCP server. Add the following config to the MCP servers config:
{
"mcpServers": {
"chrome-devtools": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest",
"--browser-url=http://127.0.0.1:9222",
"-y"
]
}
}
}This will make the Chrome DevTools MCP server automatically connect to the browser that Antigravity is using. If you are not using port 9222, make sure to adjust accordingly.
Chrome DevTools MCP will not start the browser instance automatically using this approach as as the Chrome DevTools MCP server runs in Antigravity's built-in browser. If the browser is not already running, you have to start it first by clicking the Chrome icon at the top right corner.
claude mcp add chrome-devtools npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestcodex mcp add chrome-devtools -- npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestOn Windows 11
Configure the Chrome install location and increase the startup timeout by updating .codex/config.toml and adding the following env and startup_timeout_ms parameters:
[mcp_servers.chrome-devtools]
command = "cmd"
args = [
"/c",
"npx",
"-y",
"@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest",
]
env = { SystemRoot="C:\\Windows", PROGRAMFILES="C:\\Program Files" }
startup_timeout_ms = 20_000Start Copilot CLI:
copilotStart the dialog to add a new MCP server by running:
/mcp addConfigure the following fields and press CTRL+S to save the configuration:
- Server name:
chrome-devtools - Server Type:
[1] Local - Command:
npx -y @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest
Click the button to install:
Or install manually:
Follow the MCP install guide, with the standard config from above. You can also install the Chrome DevTools MCP server using the VS Code CLI:
code --add-mcp '{"name":"@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp","command":"npx","args":["-y","@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest"],"env":{}}'Click the button to install:
Or install manually:
Go to Cursor Settings -> MCP -> New MCP Server. Use the config provided above.
droid mcp add chrome-devtools "npx -y @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest"Project wide:
gemini mcp add chrome-devtools npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestGlobally:
gemini mcp add -s user chrome-devtools npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestAlternatively, follow the MCP guide and use the standard config from above.
Go to Settings | Tools | AI Assistant | Model Context Protocol (MCP) -> Add. Use the config provided above.
The same way @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp can be configured for JetBrains Junie in Settings | Tools | Junie | MCP Settings -> Add. Use the config provided above.
In Kiro Settings, go to Configure MCP > Open Workspace or User MCP Config > Use the configuration snippet provided above.
Or, from the IDE Activity Bar > Kiro > MCP Servers > Click Open MCP Config. Use the configuration snippet provided above.
In Qoder Settings, go to MCP Server > + Add > Use the configuration snippet provided above.
Alternatively, follow the MCP guide and use the standard config from above.
Install the Chrome DevTools MCP server using the Qoder CLI (guide):
Project wide:
qodercli mcp add chrome-devtools -- npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestGlobally:
qodercli mcp add -s user chrome-devtools -- npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latestClick the button to install:
Go to Settings | AI | Manage MCP Servers -> + Add to add an MCP Server. Use the config provided above.
Your first prompt
Enter the following prompt in your MCP Client to check if everything is working:
Check the performance of https://developers.chrome.comYour MCP client should open the browser and record a performance trace.
[!NOTE]
The MCP server will start the browser automatically once the MCP client uses a tool that requires a running browser instance. Connecting to the Chrome DevTools MCP server on its own will not automatically start the browser.
Tools
If you run into any issues, checkout our troubleshooting guide.
- Input automation (8 tools)
- Navigation automation (6 tools)
- Emulation (2 tools)
- Performance (3 tools)
- Network (2 tools)
- Debugging (5 tools)
- Website MCP Tools (1 tool)
list_webmcp_tools- List available website tools across all pages (with diff)
Prompts
The server includes built-in prompts to help with WebMCP development workflows. Prompts are reusable message templates that guide AI agents through common tasks.
| Prompt | Description |
|--------|-------------|
| webmcp-dev-workflow | Step-by-step guide for building WebMCP tools with AI |
| test-webmcp-tool | Systematically test tools with edge cases and validation |
| debug-webmcp | Diagnose WebMCP connection and registration issues |
webmcp-dev-workflow
Guides you through the AI-driven development workflow for building and testing WebMCP tools.
When to use: Starting a new WebMCP tool and want step-by-step guidance through the write → hot-reload → discover → test → iterate cycle.
Arguments: None
Example:
Use the webmcp-dev-workflow prompt to help me build a search tooltest-webmcp-tool
Systematically test a WebMCP tool with various inputs including valid data, edge cases, and invalid inputs.
When to use: You have a tool ready and want to verify it handles all input scenarios correctly.
Arguments:
| Argument | Type | Required | Description |
|----------|------|----------|-------------|
| toolName | string | No | Focus testing on a specific tool |
| devServerUrl | string | No | Dev server URL (default: http://localhost:3000) |
Examples:
Use the test-webmcp-tool prompt
Use the test-webmcp-tool prompt with toolName=search_products
Use the test-webmcp-tool prompt with devServerUrl=http://localhost:5173 toolName=add_to_cartdebug-webmcp
Troubleshoot WebMCP connection issues and diagnose why tools aren't appearing or working.
When to use: Tools aren't being discovered, connections are failing, or you see "WebMCP not detected" errors.
Arguments:
| Argument | Type | Required | Description |
|----------|------|----------|-------------|
| url | string | No | Page URL to debug (default: current page) |
Example:
Use the debug-webmcp prompt with url=http://localhost:3000Configuration
The Chrome DevTools MCP server supports the following configuration option:
--browserUrl,-uConnect to a running, debuggable Chrome instance (e.g.http://127.0.0.1:9222). For more details see: https://github.com/ChromeDevTools/chrome-devtools-mcp#connecting-to-a-running-chrome-instance.- Type: string
--wsEndpoint,-wWebSocket endpoint to connect to a running Chrome instance (e.g., ws://127.0.0.1:9222/devtools/browser/). Alternative to --browserUrl.- Type: string
--wsHeadersCustom headers for WebSocket connection in JSON format (e.g., '{"Authorization":"Bearer token"}'). Only works with --wsEndpoint.- Type: string
--headlessWhether to run in headless (no UI) mode.- Type: boolean
- Default:
false
--executablePath,-ePath to custom Chrome executable.- Type: string
--isolatedIf specified, creates a temporary user-data-dir that is automatically cleaned up after the browser is closed. Defaults to false.- Type: boolean
--userDataDirPath to the user data directory for Chrome. Default is $HOME/.cache/chrome-devtools-mcp/chrome-profile$CHANNEL_SUFFIX_IF_NON_STABLE- Type: string
--channelSpecify a different Chrome channel that should be used. The default is the stable channel version.- Type: string
- Choices:
stable,canary,beta,dev
--logFilePath to a file to write debug logs to. Set the env variableDEBUGto*to enable verbose logs. Useful for submitting bug reports.- Type: string
--viewportInitial viewport size for the Chrome instances started by the server. For example,1280x720. In headless mode, max size is 3840x2160px.- Type: string
--proxyServerProxy server configuration for Chrome passed as --proxy-server when launching the browser. See https://www.chromium.org/developers/design-documents/network-settings/ for details.- Type: string
--acceptInsecureCertsIf enabled, ignores errors relative to self-signed and expired certificates. Use with caution.- Type: boolean
--chromeArgAdditional arguments for Chrome. Only applies when Chrome is launched by@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp.- Type: array
--categoryEmulationSet to false to exclude tools related to emulation.- Type: boolean
- Default:
true
--categoryPerformanceSet to false to exclude tools related to performance.- Type: boolean
- Default:
true
--categoryNetworkSet to false to exclude tools related to network.- Type: boolean
- Default:
true
Pass them via the args property in the JSON configuration. For example:
{
"mcpServers": {
"chrome-devtools": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest",
"--channel=canary",
"--headless=true",
"--isolated=true"
]
}
}
}Connecting via WebSocket with custom headers
You can connect directly to a Chrome WebSocket endpoint and include custom headers (e.g., for authentication):
{
"mcpServers": {
"chrome-devtools": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest",
"--wsEndpoint=ws://127.0.0.1:9222/devtools/browser/<id>",
"--wsHeaders={\"Authorization\":\"Bearer YOUR_TOKEN\"}"
]
}
}
}To get the WebSocket endpoint from a running Chrome instance, visit http://127.0.0.1:9222/json/version and look for the webSocketDebuggerUrl field.
You can also run npx @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest --help to see all available configuration options.
Concepts
User data directory
@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp starts a Chrome's stable channel instance using the following user
data directory:
- Linux / macOS:
$HOME/.cache/chrome-devtools-mcp/chrome-profile-$CHANNEL - Windows:
%HOMEPATH%/.cache/chrome-devtools-mcp/chrome-profile-$CHANNEL
The user data directory is not cleared between runs and shared across
all instances of @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp. Set the isolated option to true
to use a temporary user data dir instead which will be cleared automatically after
the browser is closed.
[!NOTE] When using a shared user data directory (non-isolated), the server launches Chrome with a local remote debugging port (
--remote-debugging-port=0and--remote-debugging-address=127.0.0.1) so it can auto-connect on future runs. This means any local process can attach to that port. If you prefer pipe-only mode, pass--chrome-arg=--remote-debugging-pipe(auto-connect across runs will be disabled).
Connecting to a running Chrome instance
You can connect to a running Chrome instance by using the --browser-url option. This is useful if you want to use your existing Chrome profile or if you are running the MCP server in a sandboxed environment that does not allow starting a new Chrome instance.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to connect to a running Chrome Stable instance:
Step 1: Configure the MCP client
Add the --browser-url option to your MCP client configuration. The value of this option should be the URL of the running Chrome instance. http://127.0.0.1:9222 is a common default.
{
"mcpServers": {
"chrome-devtools": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"@mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp@latest",
"--browser-url=http://127.0.0.1:9222"
]
}
}
}Step 2: Start the Chrome browser
[!WARNING]
Enabling the remote debugging port opens up a debugging port on the running browser instance. Any application on your machine can connect to this port and control the browser. Make sure that you are not browsing any sensitive websites while the debugging port is open.
Start the Chrome browser with the remote debugging port enabled. Make sure to close any running Chrome instances before starting a new one with the debugging port enabled. The port number you choose must be the same as the one you specified in the --browser-url option in your MCP client configuration.
For security reasons, Chrome requires you to use a non-default user data directory when enabling the remote debugging port. You can specify a custom directory using the --user-data-dir flag. This ensures that your regular browsing profile and data are not exposed to the debugging session.
macOS
/Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir=/tmp/chrome-profile-stableLinux
/usr/bin/google-chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir=/tmp/chrome-profile-stableWindows
"C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe" --remote-debugging-port=9222 --user-data-dir="%TEMP%\chrome-profile-stable"Step 3: Test your setup
After configuring the MCP client and starting the Chrome browser, you can test your setup by running a simple prompt in your MCP client:
Check the performance of https://developers.chrome.comYour MCP client should connect to the running Chrome instance and receive a performance report.
If you hit VM-to-host port forwarding issues, see the “Remote debugging between virtual machine (VM) and host fails” section in docs/troubleshooting.md.
For more details on remote debugging, see the Chrome DevTools documentation.
Known limitations
Operating system sandboxes
Some MCP clients allow sandboxing the MCP server using macOS Seatbelt or Linux
containers. If sandboxes are enabled, @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp is not able to start
Chrome that requires permissions to create its own sandboxes. As a workaround,
either disable sandboxing for @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp in your MCP client or use
--browser-url to connect to a Chrome instance that you start manually outside
of the MCP client sandbox.
WebMCP Integration
WebMCP enables AI agents to interact with website-specific MCP tools that are registered directly in webpages. This allows websites to expose custom functionality to AI agents via the Model Context Protocol.
How it works
When a webpage uses @mcp-b/global
to register MCP tools, @mcp-b/chrome-devtools-mcp can connect to those tools using
the Chrome DevTools Protocol. This creates a bridge between your MCP client
(like Claude Desktop, Cursor, or VS Code Copilot) and the website's tools.
Prerequisites
The webpage must have WebMCP tools registered. Websites do this by using the
@mcp-b/global package:
// Example of how a website registers tools (done by the website developer)
import '@mcp-b/global';
navigator.modelContext.registerTool({
name: 'search_products',
description: 'Search for products on this website',
inputSchema: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
query: { type: 'string', description: 'Search query' }
},
required: ['query']
},
async execute({ query }) {
// Implementation
return {
content: [{ type: 'text', text: JSON.stringify({ results: [...] }) }]
};
}
});Using WebMCP tools
Once you're on a webpage with WebMCP tools, you can use the following workflow:
1. Navigate to the webpage
Navigate to https://example.com/app2. List available tools
What tools are available on this website?The AI agent will use list_webmcp_tools to show you what functionality the
website exposes. This automatically connects to the page's WebMCP server.
3. Use the tools directly
Search for "wireless headphones" using the website's search toolThe AI agent will call the tool directly by its prefixed name (e.g., webmcp_example_com_page0_search_products).
WebMCP tools are registered as first-class MCP tools, so they appear directly in your agent's tool list.
That's it! No explicit connect or disconnect steps needed - WebMCP tools auto-connect when detected and automatically update when you navigate.
Dynamic Tool Registration
By default, WebMCP tools are automatically registered as first-class MCP tools when detected on a webpage. This means tools like search_products appear directly in your MCP client's tool list with prefixed names like webmcp_localhost_3000_page0_search_products.
MCP Client Compatibility:
| Client | Dynamic Tool Updates | Notes |
|--------|---------------------|-------|
| Claude Code | Yes | Full support for tools/list_changed |
| GitHub Copilot | Yes | Supports list changed notifications |
| Gemini CLI | Yes | Recently added support |
| Cursor | No | Use list_webmcp_tools to poll manually |
| Cline | Partial | May need manual polling with list_webmcp_tools |
| Continue | Unknown | Use list_webmcp_tools if tools don't appear |
For clients without dynamic tool support:
If your MCP client doesn't support tools/list_changed notifications, use list_webmcp_tools to manually see which tools are available, then call them directly by their prefixed names. The list_webmcp_tools tool is diff-aware to reduce context pollution:
- First call returns the full tool list
- Subsequent calls return only added/removed tools
- Use
full: trueto force the complete list
Example prompts
Here are some example prompts you can use with WebMCP-enabled websites:
What tools does this website have?Use the website's search tool to find wireless headphonesCall the website's form submission tool to fill out the contact formTroubleshooting WebMCP
- "WebMCP not detected": The current webpage doesn't have
@mcp-b/globalinstalled or no tools are registered. The page needs the WebMCP polyfill loaded. - Tool call fails: Check the tool's input schema matches your parameters.
Use
list_webmcp_toolsto see the expected input format. - Tools not appearing after navigation: WebMCP auto-reconnects when you
navigate. If the new page has different tools, call
list_webmcp_toolsagain.
Related Packages
@mcp-b/global- W3C Web Model Context API polyfill for websites@mcp-b/transports- Browser-specific MCP transports@mcp-b/react-webmcp- React hooks for MCP@modelcontextprotocol/sdk- Official MCP SDK





