@samchon/openapi
v6.0.1
Published
Universal OpenAPI to LLM function calling schemas. Transform any Swagger/OpenAPI document into type-safe schemas for OpenAI, Claude, Qwen, and more.
Maintainers
Readme
@samchon/openapi
flowchart TB
subgraph "OpenAPI Specification"
v20("Swagger v2.0") --upgrades--> emended[["OpenAPI v3.1 (emended)"]]
v30("OpenAPI v3.0") --upgrades--> emended
v31("OpenAPI v3.1") --emends--> emended
end
subgraph "LLM Function Calling"
emended --normalizes--> migration[["Migration Schema"]]
migration --"AI-Ready"--> schema{{"LLM Function Schema"}}
endTransform OpenAPI documents into LLM function calling applications.
@samchon/openapi converts OpenAPI/Swagger documents into LLM function calling schemas. With full TypeScript type safety, automatic validation, and support for every OpenAPI version, it's the simplest way to make your HTTP backend AI-callable.
Key Features
- 🌐 Multi-Provider Support: Works with OpenAI, Claude, Qwen, Llama, and other LLM providers
- 📝 Complete OpenAPI Coverage: Swagger 2.0, OpenAPI 3.0, and OpenAPI 3.1 fully supported
- 🔒 Type-Safe Validation: Built-in validation with detailed error feedback for LLM responses
- 🔄 MCP Integration: Compose function calling schemas from Model Context Protocol servers
- 📊 Emended Specification: Standardized OpenAPI v3.1 format that removes ambiguities
- ✅ Production Ready: Battle-tested with 98%+ success rates in real-world LLM applications
Live Demo:
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/e1faf30b-c703-4451-b68b-2e7a8170bce5
Watch how
@samchon/openapipowers an AI shopping chatbot with@agentica
Quick Start
npm install @samchon/openapiTransform your OpenAPI document into an LLM function calling application:
import { HttpLlm, OpenApi } from "@samchon/openapi";
// 1. Load and convert your OpenAPI document
const document: OpenApi.IDocument = OpenApi.convert(swagger);
// 2. Generate LLM function calling schemas
const application: IHttpLlmApplication = HttpLlm.application({
document,
});
// 3. Find a function to call
const func: IHttpLlmFunction | undefined = application.functions.find(
(f) => f.path === "/bbs/articles" && f.method === "post"
);
// 4. Use with any LLM provider (OpenAI, Claude, Qwen, etc.)
const completion = await llm.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o", // or claude-3-5-sonnet, qwen-plus, etc.
messages: [...],
tools: [{
type: "function",
function: {
name: func.name,
description: func.description,
parameters: func.parameters,
}
}],
});
// 5. Execute with validation
const result = await HttpLlm.execute({
connection: { host: "http://localhost:3000" },
application,
function: func,
input: llmGeneratedArgs,
});That's it! Your HTTP backend is now AI-callable across all major LLM providers.
OpenAPI Definitions
@samchon/openapi provides complete TypeScript definitions for all OpenAPI versions and introduces an "emended" OpenAPI v3.1 specification that serves as an intermediate format.
flowchart TB
v20(Swagger v2.0) --upgrades--> emended[["<b><u>OpenAPI v3.1 (emended)</u></b>"]]
v30(OpenAPI v3.0) --upgrades--> emended
v31(OpenAPI v3.1) --emends--> emended
emended --downgrades--> v20d(Swagger v2.0)
emended --downgrades--> v30d(OpenAPI v3.0)Supported Specifications:
- Swagger v2.0
- OpenAPI v3.0
- OpenAPI v3.1
- OpenAPI v3.1 (emended) - Standardized format
What is "Emended" OpenAPI?
The emended specification removes ambiguities and duplications from OpenAPI v3.1, creating a cleaner, more consistent format. All conversions flow through this intermediate format.
Key Improvements:
- Operations: Merges parameters from path and operation levels, resolves all references
- JSON Schema: Eliminates mixed types, unifies nullable handling, standardizes array/tuple representations
- Schema Composition: Consolidates
anyOf,oneOf,allOfpatterns into simpler structures
Converting Between Versions
import { OpenApi } from "@samchon/openapi";
// Convert any version to emended format
const emended: OpenApi.IDocument = OpenApi.convert(swagger); // Swagger 2.0/3.0/3.1
// Downgrade to older versions if needed
const v30: OpenApiV3.IDocument = OpenApi.downgrade(emended, "3.0");
const v20: SwaggerV2.IDocument = OpenApi.downgrade(emended, "2.0");Validating OpenAPI Documents
Use typia for runtime validation with detailed type checking:
import { OpenApi, OpenApiV3, OpenApiV3_1, SwaggerV2 } from "@samchon/openapi";
import typia from "typia";
const document: any = await fetch("swagger.json").then(r => r.json());
// Validate with detailed error messages
const result = typia.validate<
SwaggerV2.IDocument | OpenApiV3.IDocument | OpenApiV3_1.IDocument
>(document);
if (result.success) {
const emended: OpenApi.IDocument = OpenApi.convert(result.data);
} else {
console.error(result.errors); // Detailed validation errors
}Try it: Type assertion | Detailed validation
LLM Function Calling
Turn your HTTP backend into an AI-callable service. @samchon/openapi converts your OpenAPI document into function calling schemas that work with OpenAI GPT, Claude, Qwen, Llama, and other LLM providers.
Type Definitions:
Complete Example
Here's a full example showing LLM function calling with OpenAI (works identically with Claude, Qwen, etc.):
import { HttpLlm, OpenApi, IHttpLlmApplication, IHttpLlmFunction } from "@samchon/openapi";
import OpenAI from "openai";
// 1. Convert OpenAPI to LLM function calling application
const document: OpenApi.IDocument = OpenApi.convert(swagger);
const application: IHttpLlmApplication = HttpLlm.application({
document,
});
// 2. Find the function by path and method
const func: IHttpLlmFunction | undefined = application.functions.find(
(f) => f.path === "/shoppings/sellers/sale" && f.method === "post"
);
if (!func) throw new Error("Function not found");
// 3. Let OpenAI GPT call the function
const client: OpenAI = new OpenAI({ apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY });
const completion: OpenAI.ChatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful shopping assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "I want to sell Microsoft Surface Pro 9..." }
],
tools: [{
type: "function",
function: {
name: func.name,
description: func.description,
parameters: func.parameters,
}
}],
});
// 4. Execute the function call on your actual server
const toolCall = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls![0];
const result = await HttpLlm.execute({
connection: { host: "http://localhost:37001" },
application,
function: func,
input: JSON.parse(toolCall.function.arguments),
});Works with Any LLM Provider:
// OpenAI
const openai = new OpenAI({ apiKey: "..." });
// Anthropic Claude
const anthropic = new Anthropic({ apiKey: "..." });
// Alibaba Qwen via DashScope
const qwen = new OpenAI({
apiKey: "...",
baseURL: "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
});
// All use the same func.parameters schemaValidation Feedback - Fixing LLM Mistakes
The Problem: LLMs make type errors. A lot.
Even when your schema says Array<string>, GPT might return just "string". In real-world testing with OpenAI GPT-4o-mini on a shopping service:
- 1st attempt: 70% success rate ❌
- 2nd attempt (with validation feedback): 98% success rate ✅
- 3rd attempt: Never failed ✅
The Solution: Validate LLM output and send errors back for correction.
import { HttpLlm, IHttpLlmFunction, IValidation } from "@samchon/openapi";
const func: IHttpLlmFunction = application.functions[0];
// Validate LLM-generated arguments
const result: IValidation<unknown> = func.validate(llmArguments);
if (result.success === false) {
// Send detailed error feedback to LLM
return await retryWithFeedback({
message: "Type errors detected. Please correct the arguments.",
errors: result.errors, // Detailed error information
});
} else {
// Execute the validated function
const output = await HttpLlm.execute({
connection: { host: "http://localhost:3000" },
application,
function: func,
input: result.data,
});
return output;
}The validation uses typia.validate<T>(), which provides the most accurate validation and extremely detailed error messages compared to other validators:
Components | typia | TypeBox | ajv | io-ts | zod | C.V.
-------------------------|--------|-----------|-------|---------|-------|------------------
Easy to use | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Object (simple) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔
Object (hierarchical) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔
Object (recursive) | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔
Object (union, implicit) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Object (union, explicit) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌
Object (additional tags) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔
Object (template literal) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Object (dynamic properties) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Array (rest tuple) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Array (hierarchical) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔
Array (recursive) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌
Array (R+U, explicit) | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌
Array (R+U, implicit) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Array (repeated) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Array (repeated, union) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
Ultimate Union Type | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌
C.V.meansclass-validator
Human-AI Collaboration (Separating Parameters)
Sometimes you need both human input and AI-generated parameters. Use the separate option to split parameters between LLM and human:
import { HttpLlm, LlmTypeChecker } from "@samchon/openapi";
const application = HttpLlm.application({
document,
options: {
separate: (schema) =>
LlmTypeChecker.isString(schema) &&
!!schema.contentMediaType?.startsWith("image"),
},
});
const func = application.functions.find(
(f) => f.path === "/shoppings/sellers/sale" && f.method === "post"
)!;
// func.separated.llm - for AI to fill (text, numbers, etc.)
// func.separated.human - for human to provide (file uploads, images)
const result = await HttpLlm.execute({
connection: { host: "http://localhost:37001" },
application,
function: func,
input: HttpLlm.mergeParameters({
function: func,
llm: llmGeneratedArgs,
human: {
content: {
files: [...], // Human provides files
thumbnails: [...], // Human provides images
},
},
}),
});Model Context Protocol
flowchart TB
subgraph "JSON Schema Specification"
schemav4("JSON Schema v4 ~ v7") --upgrades--> emended[["OpenAPI v3.1 (emended)"]]
schema2910("JSON Schema 2019-03") --upgrades--> emended
schema2020("JSON Schema 2020-12") --emends--> emended
end
subgraph "AI Ecosystem"
emended --normalizes--> migration[["Migration Schema"]]
migration --AI-Ready--> schema{{"LLM Function Schema"}}
schema --supports--> all("All LLM Providers")
end@samchon/openapi provides better MCP function calling than using the mcp_servers property directly.
While MCP can execute server functions directly through the mcp_servers property, @samchon/openapi offers significant advantages through validation feedback and selector agent filtering for context optimization.
For example, the GitHub MCP server has 30 functions. Loading all of them via mcp_servers creates huge context that often causes AI agents to crash with hallucinations. Function calling with proper filtering avoids this problem.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/72390cb4-d9b1-4d31-a6dd-d866da5a433b
GitHub MCP server via
mcp_serversoften crashes.However, function calling to GitHub MCP with
@agenticaworks properly.
- Function calling demo: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rLlHkc24cJs
Creating MCP applications:
Use McpLlm.application() to create function calling schemas from MCP tools. The returned IMcpLlmApplication works across all LLM providers and includes validation feedback.
MCP supports all JSON schema specifications:
- JSON Schema v4, v5, v6, v7
- JSON Schema 2019-03
- JSON Schema 2020-12
import { IMcpLlmApplication, IMcpLlmFunction, IValidation, McpLlm } from "@samchon/openapi";
const application: IMcpLlmApplication = McpLlm.application({
tools: [...], // MCP tools
});
const func: IMcpLlmFunction = application.functions.find(
(f) => f.name === "create",
)!;
// Validate with detailed feedback
const result: IValidation<unknown> = func.validate({
title: "Hello World",
body: "Nice to meet you AI developers",
thumbnail: "https://wrtnlabs.io/agentica/thumbnail.jpg",
});
if (result.success) {
// Execute validated function
console.log("Valid arguments:", result.data);
} else {
// Send errors back to LLM for correction
console.error("Validation errors:", result.errors);
}[!NOTE]
You can also compose
ILlmApplicationfrom a TypeScript class usingtypia.https://typia.io/docs/llm/application
import { ILlmApplication } from "@samchon/openapi"; import typia from "typia"; const app: ILlmApplication = typia.llm.application<YourClassType>();
Utilization Cases
Agentica
https://github.com/wrtnlabs/agentica
Agentic AI framework that converts OpenAPI documents into LLM function calling schemas. Uses @samchon/openapi to transform backend REST APIs into callable functions with automatic parameter validation and type-safe remote execution.
import { Agentica, assertHttpController } from "@agentica/core";
import OpenAI from "openai";
import typia from "typia";
import { MobileFileSystem } from "./services/MobileFileSystem";
const agent = new Agentica({
vendor: {
api: new OpenAI({ apiKey: "********" }),
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
},
controllers: [
// Functions from TypeScript class
typia.llm.controller(
"filesystem",
MobileFileSystem(),
),
// Functions from Swagger/OpenAPI
// Uses @samchon/openapi under the hood
assertHttpController({
name: "shopping",
document: await fetch(
"https://shopping-be.wrtn.ai/editor/swagger.json",
).then(r => r.json()),
connection: {
host: "https://shopping-be.wrtn.ai",
headers: { Authorization: "Bearer ********" },
},
}),
],
});
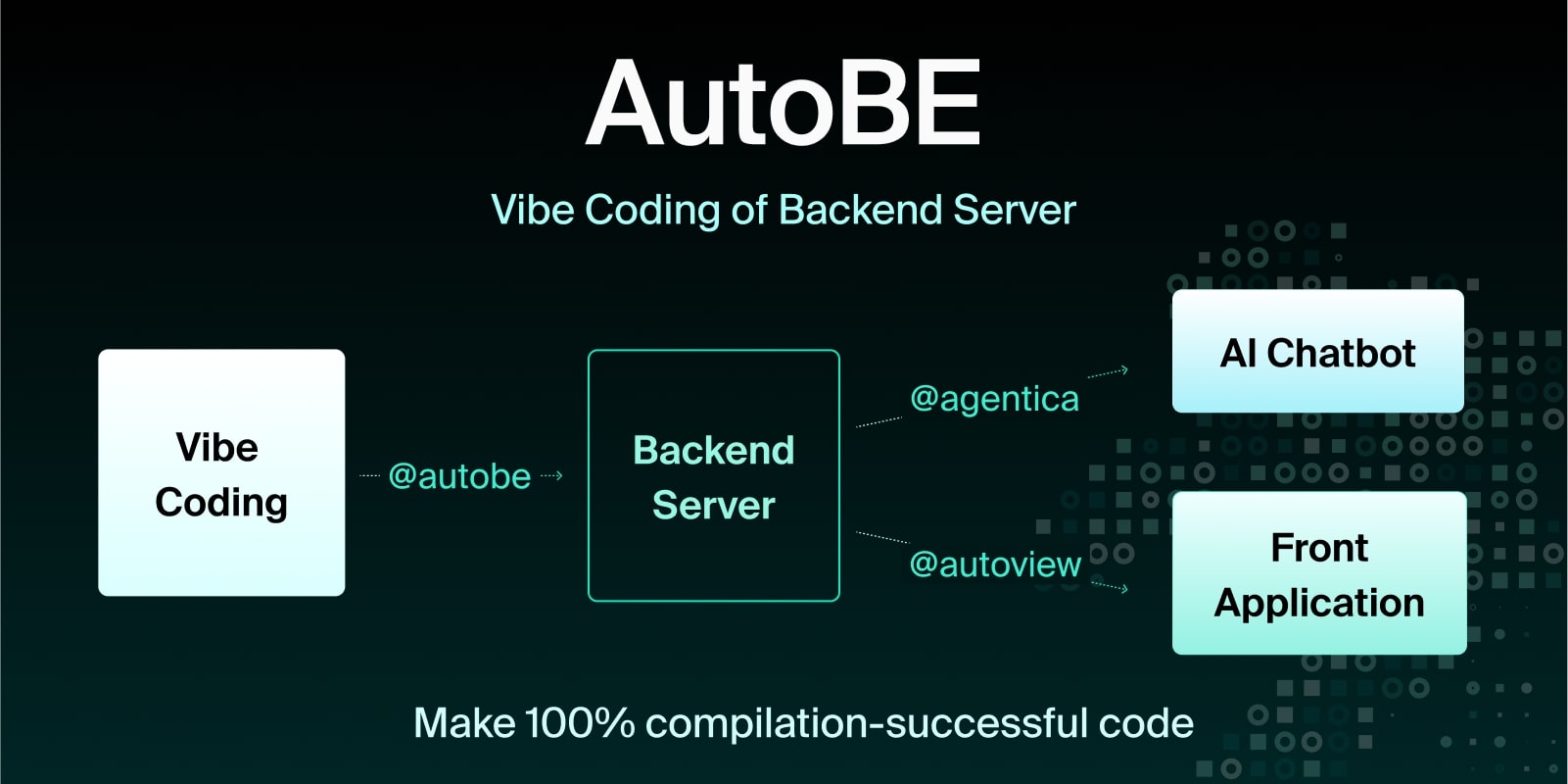
await agent.conversate("I wanna buy MacBook Pro");AutoBE
https://autobe.dev
AI backend code generator achieving 100% compilation success by using function calling to construct compiler AST instead of generating code text. For API specification design, uses @samchon/openapi types - AI calls compiler functions to build OpenAPI document structures that define REST endpoints and request/response schemas.
import { MicroAgentica } from "@agentica/core";
import { OpenApi } from "@samchon/openapi";
const agent = new MicroAgentica({
vendor: {
api: new OpenAI({ apiKey: "********" }),
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
},
controllers: [
// Compiler functions that receive/produce OpenApi.IDocument
typia.llm.controller(
"api",
new OpenApiWriteApplication(),
),
],
});
await agent.conversate("Design API specification and generate backend app.");
class OpenApiWriteApplication {
// LLM calls this function with OpenApi.IDocument structure
public async write(document: OpenApi.IDocument): Promise<void> {
// Compiler validates schema structure before code generation
...
}
}License
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2024 Jeongho Nam
For detailed API documentation, visit: https://samchon.github.io/openapi/api/