@sejhey/react-i18n
v0.7.0
Published
The SejHey i18n SDK for React
Maintainers
Readme
SejHey i18n for React
SejHey is a powerful and cost effective alternative to Crowdin, Phrase, Lokalise and other i18n platforms.
This library provides a full i18n solution for React applications, allowing you to easily manage translations and support multiple languages. Push translations to SejHey and fetch them dynamically in your React app. Collaborate with your team to manage translations efficiently. Publish changes instantly without redeploying your app.
To learn more about SejHey, visit SejHey Docs.
✨ Features
- React context provider via
SejHeyProvider - Translation hook
useTranslate - Component-based translation with
<T /> - In-context editing support (Even in production)
- Static or CDN-based file loading
- Lazy language loading
- Custom loader component support
- SSR Support for Next.js
🚀 Installation
npm install @sejhey/react-i18n🧩 Usage
1. Wrap your app in the SejHeyProvider
Minimal setup with CDN Loader and In Context Editor.
import { SejheyI18n, SejHeyProvider, useTranslate, T } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
/* Create the i18n instance */
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({ defaultLanguage: 'en' })
//Fetch translations from SejHey CDN, always up to date. This will use cdn.sejhey.com/projects/**sejheyProjectId**/**otaEnvName**/manifest.json. Replace with your projectId.
.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
//This enables in-context editing by adding ?in_context=true. In-context means that your project members can edit translations directly on the web page.
.useInContextEditor({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
//Place a language picker on your site automatically
.useLanguagePicker()
/* Wrap you app with <SejHeyProvider> */
export default function MyApp() {
return (
<SejHeyProvider i18n={i18n}>
<AnotherComponent />
</SejHeyProvider>
)
}
/* Now use translations like this */
const AnotherComponent = () => {
const { t } = useTranslate()
return (
<>
<h1>{t('welcome_message')}</h1>
{/* Or if you prefer a component */}
<T keyName='welcome_message' />
</>
)
}You can also use static files as a backup or alternative to the CDN
const en = () => import('../locales/en.json')
const fr = () => import('../locales/fr.json')
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({ defaultLanguage: 'en' })
...
.useStaticLoader({ files: { en: en, fr: fr } }) //Treated as fallback if CdnLoader would fail2. Pluralization and parameters
SejHey supports pluralization and parameters both for useTranslate and the <T /> component.
import { useTranslate } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
export function Welcome() {
const { t } = useTranslate()
return (
<>
{/* Will be outputted as Patrik has one new message */}
{t('welcome_message_plural', { count: 1, name: 'Patrik' })}
{/* Same as above, but with T */}
<T
keyName='welcome_message_plural'
params={{ count: 1, name: 'Patrik' }}
/>
{/* Will be outputted as Anders has five new messages */}
{t('welcome_message_plural', { count: 5, name: 'Anders' })}
{/* Same as above, but with T */}
<T
keyName='welcome_message_plural'
params={{ count: 5, name: 'Anders' }}
/>
</>
)
}3. Next.js and SSR Support
SejHey provides full support for server-side rendering (SSR) in Next.js applications. This enables translations to be fetched and cached on your server during the initial render. This means that users will see the correct translations immediately, without any flickering or loading states.
SejHey also caches translations locally on your server for concurrent requests. This is implemented using a SWR (Stale While Revalidate) approach. This means that translation updates are propagated within a few seconds to your application without compromising any caching performance.
Understanding Next.js Routing
Next.js offers two routing systems:
Page Router (Pages Directory): The original routing system using a
pages/directory. Each file inpages/becomes a route. Uses_app.tsxfor app-wide configuration andgetInitialPropsfor SSR data fetching.App Router (App Directory): The newer routing system introduced in Next.js 13+ using an
app/directory. Provides better performance with React Server Components, improved layouts, and built-in loading/error states. Useslayout.tsxfor app-wide configuration and supports both Server and Client Components.
Which one should you use?
- Use App Router for new projects (Next.js 13.4+) as it's the recommended approach with better performance and features.
- Use Page Router if you're working with an existing Next.js project or need features that aren't yet available in App Router.
Page Router Setup
The Page Router uses the pages/ directory structure and requires setup in pages/_app.tsx.
Recommended File Structure:
your-nextjs-app/
├── pages/
│ ├── _app.tsx # Main app wrapper (setup SejHey here)
│ ├── index.tsx # Home page
│ └── about/
│ └── index.tsx # About page
└── package.jsonSetup Instructions:
- Create or update
pages/_app.tsx:
import type { AppContext, AppProps } from 'next/app'
import {
SejheyI18n,
SejHeyProvider,
getSejHeyInitialProps
} from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
// Create the i18n instance
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({
defaultLanguage: 'en'
})
.useCdnLoader({
sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX',
otaEnvName: 'production'
})
.useInContextEditor({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
.useLanguagePicker()
// Define your App component
export default function MyApp({
Component,
pageProps,
serialized
}: AppProps & { serialized?: any }) {
return (
<SejHeyProvider i18n={i18n} serialized={{serialized}}>
<Component {...pageProps} />
</SejHeyProvider>
)
}
// Enable SSR - this fetches and caches translations on the server
MyApp.getInitialProps = async (appContext: AppContext) =>
getSejHeyInitialProps(MyApp, appContext, i18n)- Use translations in your pages:
// pages/index.tsx
import { useTranslate, T } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
export default function Home() {
const { t, changeLanguage } = useTranslate()
return (
<div>
<h1>{t('welcome_message')}</h1>
<T keyName='greeting' params={{ name: 'John' }} />
<button onClick={() => changeLanguage('fr')}>
Switch to French
</button>
</div>
)
}App Router Setup
The App Router uses the app/ directory structure and requires a more modular setup with separate client and server components.
Recommended File Structure:
your-nextjs-app/
├── app/
│ ├── layout.tsx # Root layout (uses SejHey server setup)
│ ├── page.tsx # Home page
│ └── about/
│ └── page.tsx # About page
├── sejhey/
│ ├── client.tsx # Client-side SejHey wrapper
│ ├── server.tsx # Server-side SejHey instance
│ ├── shared.tsx # Shared i18n configuration
└── package.jsonSetup Instructions:
- Create
sejhey/shared.tsxto define your i18n configuration:
import { SejheyI18n } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
export const getI18n = () => {
return new SejheyI18n({
defaultLanguage: 'en'
})
.useCdnLoader({
sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX',
otaEnvName: 'production'
})
.useInContextEditor({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
.useLanguagePicker({ position: 'bottom-right' })
}- Create
sejhey/server.tsxfor server-side usage:
import { createServerInstance } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
import { getI18n } from './shared'
import { headers } from 'next/headers'
const i18n = getI18n()
export const { T, translate, sejheyInstance } = await createServerInstance(
i18n,
{ headers } //By providing headers to the server instance, the users preffered language will automatically be fetched from cookie or header.
)- Create
sejhey/client.tsxfor client-side provider:
'use client' //This tells nextjs this is a "client component", see nextjs documentation for more info
import { SejHeyProvider, SejHeyServerSerializedInstance } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
import { getI18n } from './shared'
import { useRouter } from 'next/navigation'
import { useEffect } from 'react'
const i18n = getI18n()
export default function ClientWrapper({
children,
serialized
}: {
children: React.ReactNode
serialized: SejHeyServerSerializedInstance
}) {
const router = useRouter()
useEffect(() => {
// Ensure server components refresh after language change
const unsubscribe = i18n.on('language_change_complete', () => {
router.refresh()
})
return () => unsubscribe()
}, [i18n, router])
return (
<SejHeyProvider i18n={i18n} serialized={serialized}>
{children}
</SejHeyProvider>
)
}- Update
app/layout.tsx(root layout):
import { ReactNode } from 'react'
import ClientWrapper from '@/sejhey/client'
import { sejheyInstance } from '@/sejhey/server'
import { headers } from 'next/headers'
export default async function RootLayout({
children
}: {
children: ReactNode
}) {
// Initialize SejHey on the server with request headers
await sejheyInstance.init(headers)
const serialized = sejheyInstance.serialized()
return (
<html>
<body>
<ClientWrapper serialized={serialized}>
{children}
</ClientWrapper>
</body>
</html>
)
}- Use translations in your pages:
For Server Components (default in App Router):
// app/page.tsx
import { T, translate } from '@/sejhey/server'
export default async function Home() {
// Server-side translation
const welcomeText = translate('welcome_message')
return (
<div>
<h1>{welcomeText}</h1>
<T keyName='greeting' params={{ name: 'John' }} />
</div>
)
}For Client Components:
// app/client-page.tsx
'use client'
import { useTranslate, T } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
export default function ClientPage() {
const { t, changeLanguage } = useTranslate()
return (
<div>
<h1>{t('welcome_message')}</h1>
<T keyName='greeting' params={{ name: 'John' }} />
<button onClick={() => changeLanguage('fr')}>
Switch to French
</button>
</div>
)
}4. Changing language
You can change language easily by using the hook useTranslate. It can be done like this
const MyComponent = () => {
const { t, changeLanguage, availableLanguages, currentLanguage } =
useTranslate()
return <div onClick={() => changeLanguage('fr')}>Change to french</div>
}📦 CDN Loader
The CDN Loader allows you to fetch translations from the SejHey CDN dynamically. This ensures that your translations are always up to date without requiring a full redeploy of your application. Translations from the CDN is hosted using Cloudflare edge servers. This means that they always are delivered with low latency and high availability.
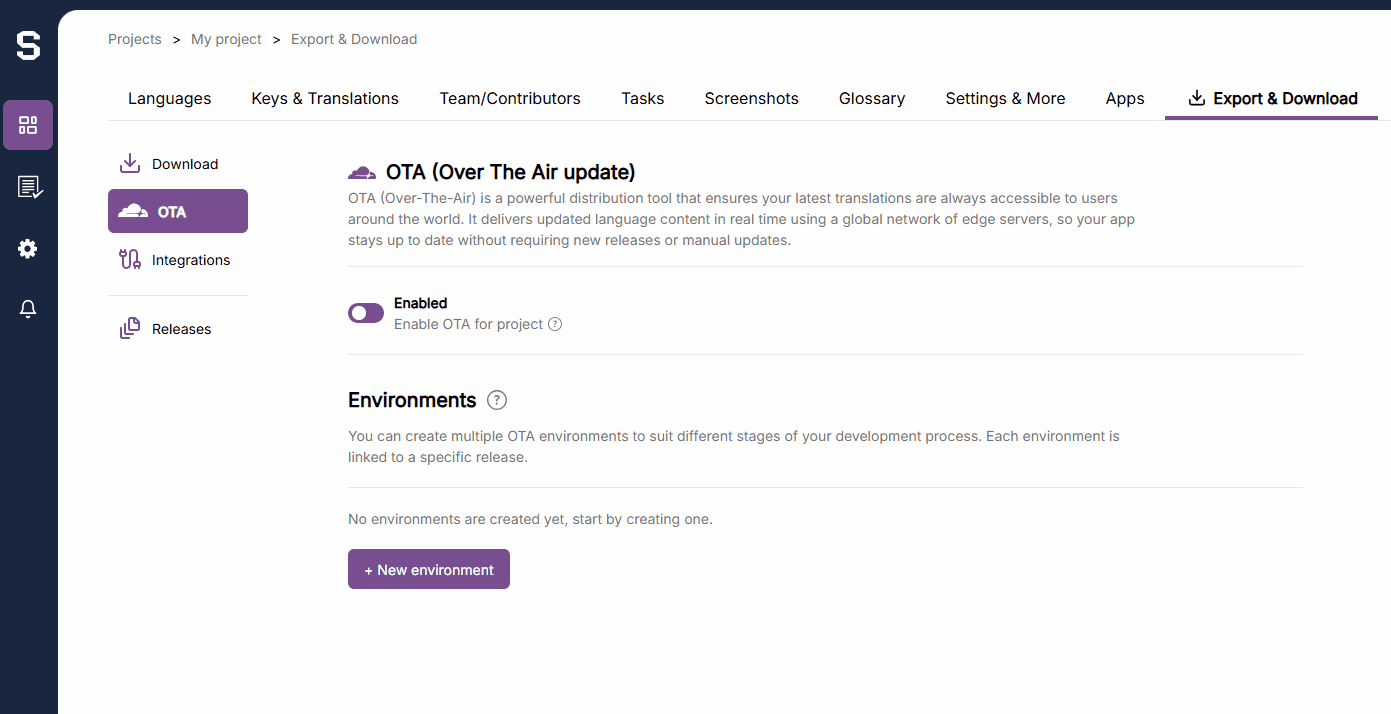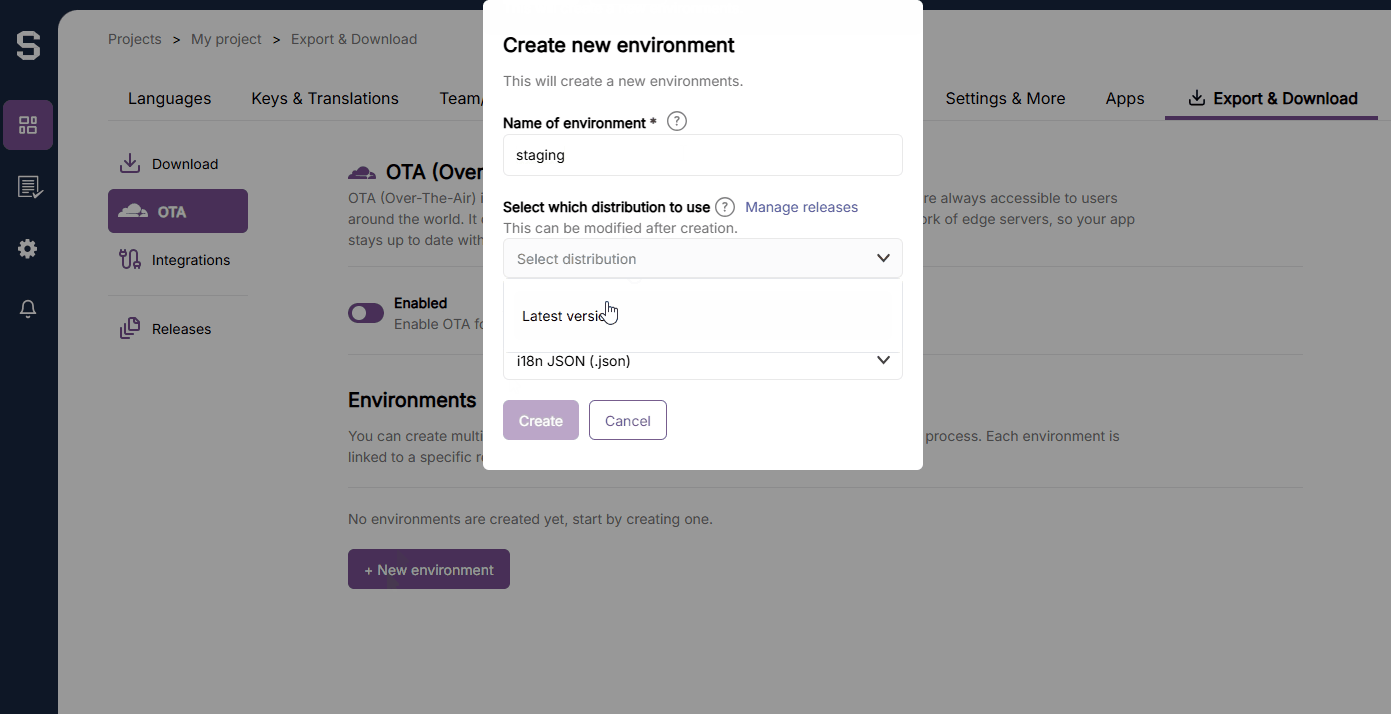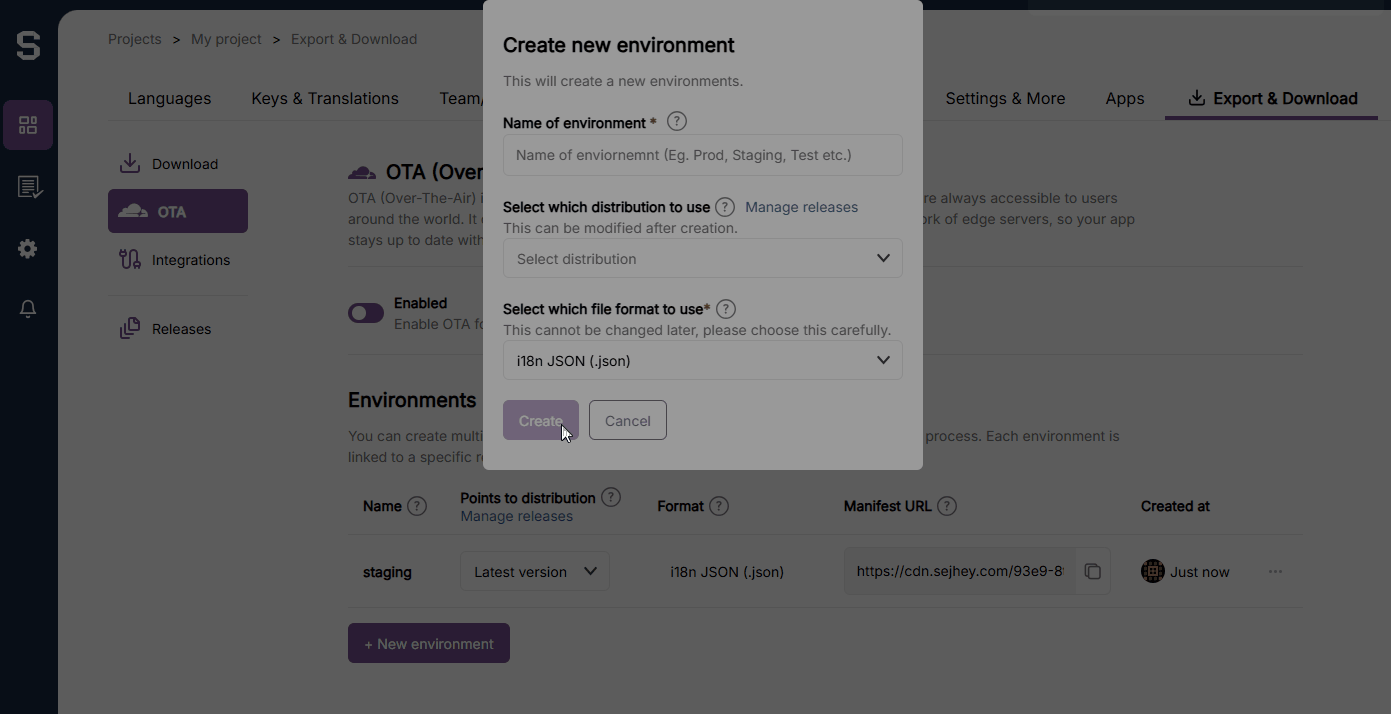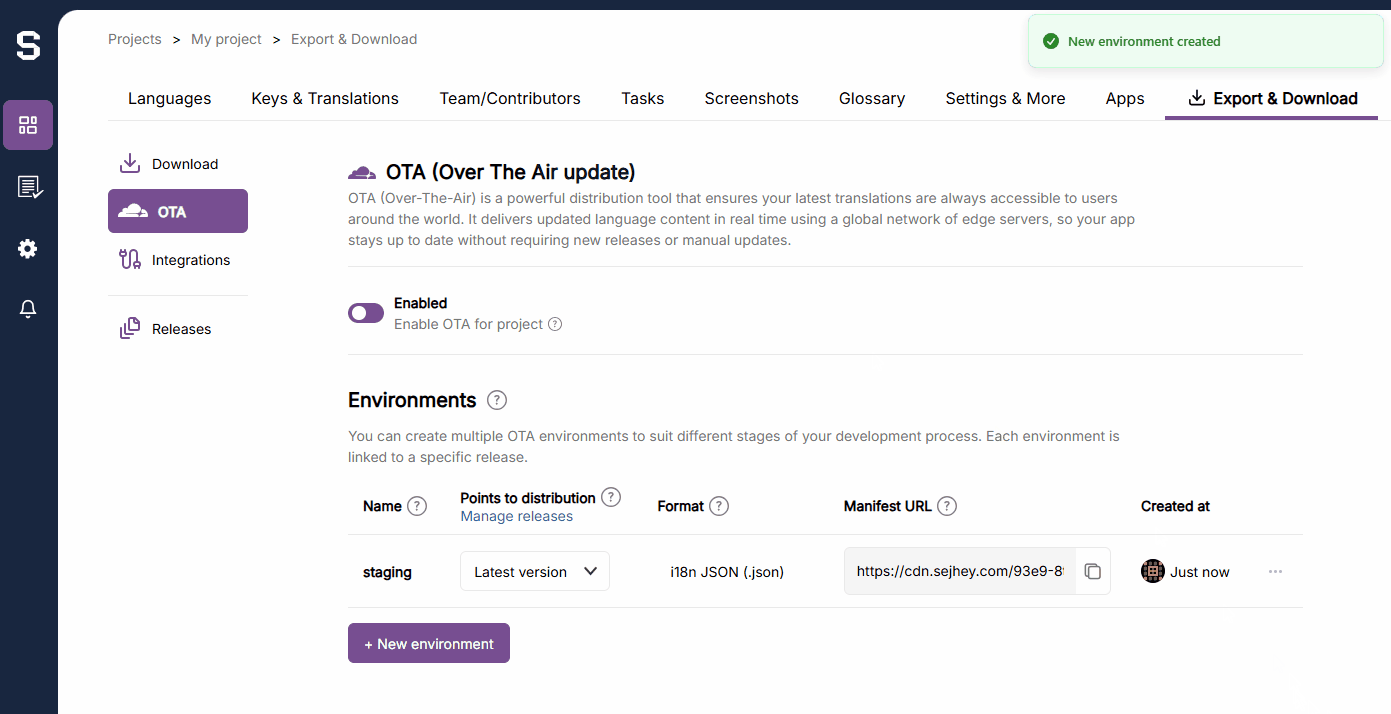
You can set which Environment that the application should point towards. This enables you to have different environments for development, staging, and production. This is set by using the otaEnvName option in the CDN loader.
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({ defaultLanguage: 'en' }).useCdnLoader({
sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX',
otaEnvName: 'staging'
}) // Specific environment. Defined in SejHey dashboard.To create a new environment, follow this instruction from within the SejHey dashboard. Note that the format must be i18n-JSON.
✏️ In-Context Editor
You easily enable in the in-context editor by adding the .useInContextEditor() in the configuration. This enables in-context editing by adding ?in_context=true to the URL. The in-context editor allow translations to be edited on the web-page directly.
Note: When In-Context is enabled, the translators must still authenticate themselves towards SejHey and translations can only be edited if the user has the appropriate permissions.
You can customize the query parameter to enable in-context by providing your own parameter name:
.useInContextEditor({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX', enableByQueryParam: 'my_custom_param' })This would enable in_context by adding ?my_custom_param=true to the URL.
Creating keys
If the logged in user has the appropriate permissions, they can create new translation keys directly from the in-context editor. This allows for a more streamlined workflow, as translators can add missing keys on the fly without needing to switch back to the main application.
Language detection
By default, language detection is enabled in this plugin. The default order is defined as. "querystring","nextjs", "cookie", "localStorage", "path", "subdomain", "htmlTag", "navigator". This can be customized or disabled, see languageDetectionSettings in the API documentation for reference.
📚 Namespaces
Namespaces allow you to organize your translations into logical groups. This is useful for large applications where you want to split translations by feature, module, or component. Namespaces help reduce bundle size by loading only the translations you need.
Setting namespaces at initialization
You can specify which namespaces to load when creating the i18n instance:
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({
defaultLanguage: 'en',
loadedNamespaces: ['common', 'dashboard', 'settings']
})
.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })All specified namespaces will be loaded when the i18n instance is initialized or when the language changes.
Adding and removing namespaces dynamically
You can add or remove namespaces at runtime using the i18n instance methods:
// Add a namespace (will be loaded immediately)
await i18n.addNamespace('notifications')
// Remove a namespace
i18n.removeNamespace('settings')Note: When using namespaces with React, you'll need to access the i18n instance. You can do this by storing the instance in a variable that's accessible to your components, or by using a context if needed.
Using namespaced translation keys
There are two ways to use namespaces with translation keys:
Option 1: Pass namespace to useTranslate hook
You can pass a namespace directly to the useTranslate hook. This will automatically prefix all translation keys with that namespace:
// All keys that will belongs to the namespace common will be available
const { t } = useTranslate('common')
// No need to prefix the key - it's automatically added
{t('welcome_message')} // Translates to 'common:welcome_message'
{t('greeting', { name: 'John' })} // Translates to 'common:greeting'
Example: Lazy loading namespaces
You can load namespaces on-demand for better performance. The useTranslate hook will automatically add the namespace when you pass it:
// Create i18n instance in a separate file or at module level
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({
defaultLanguage: 'en',
loadedNamespaces: ['common'] // Load common namespace initially
})
.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
// In your component - namespace is automatically loaded when used
const MyComponent = () => {
// Passing 'notifications' will automatically add it to namespaces to load
const { t } = useTranslate('notifications')
return (
<div>
{/* No need to prefix with 'notifications:' - it's automatic */}
<p>{t('new_message')}</p>
<p>{t('unread_count', { count: 5 })}</p>
</div>
)
}Alternatively, you can manually manage namespaces:
// Create i18n instance in a separate file or at module level
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({
defaultLanguage: 'en',
loadedNamespaces: ['common']
})
.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
// In your component
const MyComponent = () => {
const { t } = useTranslate()
const [namespaceLoaded, setNamespaceLoaded] = useState(false)
const loadNotifications = async () => {
await i18n.addNamespace('notifications')
setNamespaceLoaded(true)
}
return (
<div>
{!namespaceLoaded && (
<button onClick={loadNotifications}>Load notifications</button>
)}
{namespaceLoaded && (
<p>{t('new_message')}</p>
)}
</div>
)
}🗂 Static Translations File Format
If you provide static translation files, they must follow flat JSON-i18n format, e.g.:
{
"welcome_message": "Welcome to SejHey!",
//If params are present
"greeting_message": "Hello, {{name}}!",
//If plural use suffix _one, _other etc, and the variable {{count}}
"welcome_message_plural_one": "You have one message",
"welcome_message_plural_other": "You have {{count}} messages"
}If you are exporting files from SejHey, this option format is called i18n JSON.
Note: When using namespaces, translation keys in your JSON files should be prefixed with the namespace and a colon (e.g., "common:welcome_message"). However, when using the CDN loader, SejHey will automatically organize translations by namespace, so you don't need to prefix keys in the exported files.
📘 API Reference: SejheyI18n
new SejheyI18n(config)
Creates a new SejHey i18n instance.
Parameters:
config: DefaultConfigdefaultLanguage(string, required): The initial language to use (e.g.,"en").loadedNamespaces(string[], optional): Array of namespace names to load initially. These namespaces will be fetched when the i18n instance is initialized or when the language changes. Example:['common', 'dashboard'].languageDetectionSettings(LanguageDetectorConfig, optional):detectionOrder?: DetectorAlternative[]— Detection order:"querystring","nextjs","cookie","localStorage","path","subdomain","htmlTag","navigator". You can customize which ways the plugin uses to detect the current language of their choice.queryParamName?: string— Name of query parameter to detect language if querystring is used. Defaults to locale. Eg?locale=de.disable?: boolean— Disable detection entirely.
fallbackSettings(FallbackConfig, optional):show:'key' | 'empty' | 'fallback_language'— What to display if translation is missing.fallbackLanguage?: string— Language to use as fallback.
Chainable Instance Methods
The SejheyI18n instance implements these methods to configure the functionality:
.useCdnLoader(options?: CdnLoaderOptions)
Fetch translations dynamically from SejHey CDN.
Options:
sejheyProjectId(string, required if using SejHey CDN): Your SejHey project ID (found in your SejHey project under Settings & More -> Settings).otaEnvName(string, optional): Environment name (e.g.,"production","staging"). This is defined from the SejHey project underExport & Download -> OTA -> Environments. If not provided, thedefaultenv will be used.baseUrl(string, optional): Custom base URL for CDN. If provided,sejheyProjectIdandotaEnvNameshould not be used.
// Using SejHey CDN
i18n.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX', otaEnvName: 'production' })
// Using custom base URL
i18n.useCdnLoader({ baseUrl: 'https://cdn.example.com/translations/' }).useStaticLoader(options: { files: StaticFileLoader })
Define fallback static translations (bundled with your app).
files: Object where keys are language codes and values are:- A function returning
Promise<FlatJson>(lazy import) - Or a
Promise<FlatJson>directly.
- A function returning
i18n.useStaticLoader({
files: {
en: () => import('../locales/en.json'),
fr: () => import('../locales/fr.json')
}
}).useInContextEditor(options: InContextEditorSettings)
Enable in-context editing for translators.
Note: By enabling this, you do not increase the bundle size. This part of the bundle is dynamically loaded only when needed.
Options:
sejheyProjectId(string, required): Your SejHey project ID (found in your SejHey project under Settings & More -> Settings).enableByQueryParam?: string— Query parameter that activates the editor (defaults to"in_context"). E.g.,?in_context=true.
i18n.useInContextEditor({
sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX',
enableByQueryParam: 'in_context'
}).useLanguagePicker(options?: LanguagePickerSettings)
Automatically render a floating language picker on your site.
position?: 'top-left' | 'top-right' | 'bottom-left' | 'bottom-right'onChangeLanguage?: (lang: string) => voidfixedLocales?: string[]— Restrict available locales.
i18n.useLanguagePicker({ position: 'bottom-right' }).addNamespace(namespace: string): Promise<void>
Dynamically add a namespace to be loaded. The namespace will be fetched immediately for the current language.
Parameters:
namespace(string, required): The namespace name to add (e.g.,"notifications").
await i18n.addNamespace('notifications').removeNamespace(namespace: string): void
Remove a namespace from the list of namespaces to fetch. This only removes one occurrence if the namespace was added multiple times.
Parameters:
namespace(string, required): The namespace name to remove.
i18n.removeNamespace('settings')<SejHeyProvider />
React provider to wrap your app.
Props:
i18n(ISejHeyCoreWrapper, required): Instance created vianew SejheyI18n().serialized?: any: Preloaded translations (e.g., from SSR). See more under getSejHeyInitialProps.children: React.ReactNode: Your app components.suspenseComponent?: React.ReactNode: Optional loading fallback (e.g., spinner) that is shown before translations are loaded.
Example:
<SejHeyProvider i18n={i18n}>
<App />
</SejHeyProvider>useTranslate(namespace?: string)
React hook returning translation utilities.
Parameters:
namespace(string, optional): If provided, all translation keys will be automatically prefixed with this namespace. The namespace will also be added to the list of namespaces to load if not already loaded.
Returns:
t(key: string, params?: OptionsParams, defaultValue?: string, context?: string): string— Translation function. If a namespace was provided touseTranslate, keys without a:will be automatically prefixed with that namespace.changeLanguage(lang: string): void— Change language dynamically.currentLanguage: string— Active language code.availableLanguages: string[]— All available languages.
Examples:
// Without namespace
const { t, changeLanguage } = useTranslate()
return <p>{t('welcome_message', { name: 'John' })}</p>
// With namespace - keys are automatically prefixed
const { t } = useTranslate('common')
return <p>{t('welcome_message')}</p> // Translates 'common:welcome_message'
// You can still use fully qualified keys
const { t } = useTranslate('common')
return <p>{t('dashboard:user_count', { count: 5 })}</p> // Uses 'dashboard:user_count' as-is<T /> Component
JSX component alternative to t() function.
Props:
keyName: string— Translation key.params?: OptionsParams— Dynamic variables{ name: 'John' }.defaultValue?: string— Fallback if missing.
Example:
<T keyName='welcome_message' params={{ name: 'John' }} />getSejHeyInitialProps(App, appContext, i18n)
Note: This function is specifically for Next.js Page Router (Pages Directory). For App Router setups, use createServerInstance as shown in the App Router Setup section above.
For SSR in Page Router, preloads translations on the server.
Parameters:
App(Component, required): The Next.js App component.appContext(AppContext, required): The Next.js app context.i18n(SejheyI18n, required): The SejHey i18n instance.
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({ defaultLanguage: 'en' })
.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX', otaEnvName: 'production' })
export default function MyApp({ Component, pageProps, serialized }: { Component: any, pageProps: any, serialized?: any }) {
return (
<SejHeyProvider i18n={i18n} serialized={serialized}>
<Component {...pageProps} />
</SejHeyProvider>
);
}
MyApp.getInitialProps = async (appContext: import('next/app').AppContext) =>
getSejHeyInitialProps(MyApp, appContext, i18n);See the Page Router Setup section above for complete setup instructions.
createServerInstance(i18n, options)
Note: This function is specifically for Next.js App Router (App Directory). For Page Router setups, use getSejHeyInitialProps as shown in the Page Router Setup section above.
Creates a server-side instance for App Router that enables SSR support. This should be used in Server Components and the root layout.
Parameters:
i18n(SejheyI18n, required): The SejHey i18n instance created withnew SejheyI18n().options(object, required):headers: Next.js headers function (fromnext/headers). Used for language detection from request headers.
Returns:
An object with:
T: Server Component for translationstranslate(key: string, params?: OptionsParams): string: Server-side translation functionsejheyInstance: Server instance with methods:init(headers): Initialize and fetch translations (call in layout)serialized(): Get serialized translations for client hydration
// sejhey/server.tsx
import { createServerInstance } from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
import { getI18n } from './shared'
import { headers } from 'next/headers'
const i18n = getI18n()
export const { T, translate, sejheyInstance } = await createServerInstance(
i18n,
{ headers }
)See the App Router Setup section above for complete setup instructions.
🔧 Example Usage
For complete Next.js setup instructions, see the Next.js and SSR Support section above, which includes detailed guides for both:
- Page Router Setup - For Next.js projects using the
pages/directory - App Router Setup - For Next.js 13+ projects using the
app/directory
Quick Example (Page Router):
import {
SejheyI18n,
SejHeyProvider,
getSejHeyInitialProps
} from '@sejhey/react-i18n'
const en = () => import('../locales/en.json')
const fr = () => import('../locales/fr.json')
const i18n = new SejheyI18n({
defaultLanguage: 'en'
})
.useCdnLoader({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX', otaEnvName: 'production' })
.useStaticLoader({ files: { en, fr } })
.useInContextEditor({ sejheyProjectId: 'XXXX-XXXX' })
.useLanguagePicker()
export default function MyApp({
Component,
pageProps,
serialized
}: {
Component: any
pageProps: any
serialized?: any
}) {
return (
<SejHeyProvider i18n={i18n} serialized={serialized}>
<Component {...pageProps} />
</SejHeyProvider>
)
}
MyApp.getInitialProps = async (appContext: import('next/app').AppContext) =>
getSejHeyInitialProps(MyApp, appContext, i18n)For App Router examples, see the App Router Setup section above.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.