@vs-org/command-parser
v0.0.2
Published
This is simple command parser for command line node applications designed to handle inline argument, inline named argument, user input, user choices.
Downloads
2
Maintainers
Readme
vs-command-parser
VS command parser can be used to simplify command line argument handling.
VS command parser can support handling for inline command line arguments with both node index.js {arguments} and npm run command {arguments}.
VS command parser can parse inline arguments, inline named arguments, user input, user choice inputs.
Usage
Inline command line arguments
a) Parsing inline argument is tricky as it depends on what sequence user is using. b) It can be marked as true, but user provided sequence only be assigned to options from configuration sequencially. c) Value meant for option 2 can be assigned to option 1, as it was provided in that sequence. d) Recommendation is to use
namedOptions.
// module
const VsCommandParser = require("@vs-org/command-parser").default;
// CJS
import VsCommandParser from "@vs-org/command-parser";
(async () => {
const commandParser = new VsCommandParser({
options: {
1: {
description: "option 1 description"
},
2: {
description: "option 2 description"
}
}
});
const ans = await commandParser.parse();
console.log(ans);
})();
// command
npm run command option1Val opion2Val
// output
{
'1': {
value: 'option1Val',
validationMsg: '',
description: 'option 1 description'
},
'2': {
value: 'option2Val',
validationMsg: '',
description: 'option 2 description'
}
}
Named command line arguments
a) When using named options, sequence does not matter. b) Keep in mind when spaces are used in option name and value there would be unexpected results if value is empty. c) As long as there is value after space for option it will be properly assigned to option.
// module
const VsCommandParser = require("@vs-org/command-parser").default;
// CJS
import VsCommandParser from "@vs-org/command-parser";
(async () => {
const commandParser = new VsCommandParser({
namedOptions: {
1: {
description: "option 1 description"
},
2: {
description: "option 2 description"
}
}
});
const ans = await commandParser.parse();
console.log(ans);
})();
// command
npm run command 1=option1Val 2=opion2Val
npm run command 1 = option1Val 2 = opion2Val
// output
{
'1': {
value: 'option1Val',
validationMsg: '',
description: 'option 1 description'
},
'2': {
value: 'option2Val',
validationMsg: '',
description: 'option 2 description'
}
}
// command
npm run command 1=option1Val 2=opion2Val
// Output
{
'1': { value: 'option1Val', validationMsg: '', description: '' },
'2': { value: 'option2Val', validationMsg: '', description: '' }
}
// command
npm run command 1 = 2 = opion2Val
// Output
Throws Error (Error: 1 cannot have 2 as value. If you wish to provide empty value, either use named option at last position or mark this option as not required and don't provide it)
// As value for first named option is name of second option. That is not allowed
User input option
a) If there are some arguments needs an user input like question and answer use this. b) Note blank answer can be provided only for optional questions. If
requiredis true for question command parser will keep on asking question
// module
const VsCommandParser = require("@vs-org/command-parser").default;
// CJS
import VsCommandParser from "@vs-org/command-parser";
(async () => {
const commandParser = new VsCommandParser({
userInputOptions: {
1: { question: "que 1?", description: "option 1 description" },
2: { question: "que 2?", description: "option 2 description" }
}
});
const ans = await commandParser.parse();
console.log(ans);
})();
// command
npm run command
// output without providing any answer
{
'1': {
question: 'que 1?',
value: '',
description: 'option 1 description',
validationMsg: ''
},
'2': {
question: 'que 2?',
value: '',
description: 'option 2 description',
validationMsg: ''
}
}
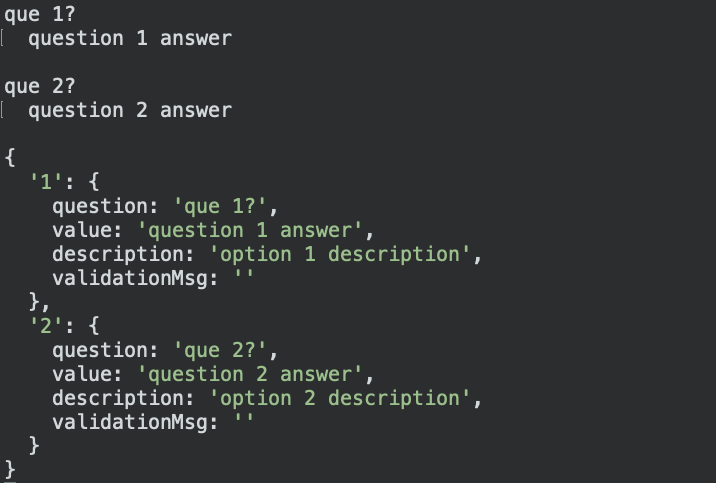
// With answers
{
'1': {
question: 'que 1?',
value: 'question 1 answer',
description: 'option 1 description',
validationMsg: ''
},
'2': {
question: 'que 2?',
value: 'question 2 answer',
description: 'option 2 description',
validationMsg: ''
}
}
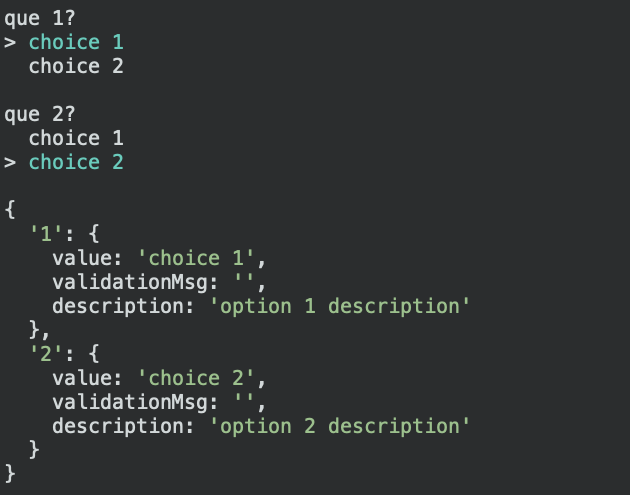
User choice option
a) If there are need for options then use this option. b) User will be presenteed with
choicesfrom config.
// module
const VsCommandParser = require("@vs-org/command-parser").default;
// CJS
import VsCommandParser from "@vs-org/command-parser";
(async () => {
const commandParser = new VsCommandParser({
userChoiceOptions: {
1: {
question: "que 1?",
choices: ["choice 1", "choice 2"],
description: "option 1 description"
},
2: {
question: "que 2?",
choices: ["choice 1", "choice 2"],
description: "option 2 description"
}
}
});
const ans = await commandParser.parse();
console.log(ans);
})();
// command
npm run command
// output
{
'1': {
value: 'choice 1',
validationMsg: '',
description: 'option 1 description'
},
'2': {
value: 'choice 2',
validationMsg: '',
description: 'option 2 description'
}
}
Help
a) If description is provided for each option, then it will be used in help command. b) Help is reserved keyword, command parser will throw error when
helpis used as option key.
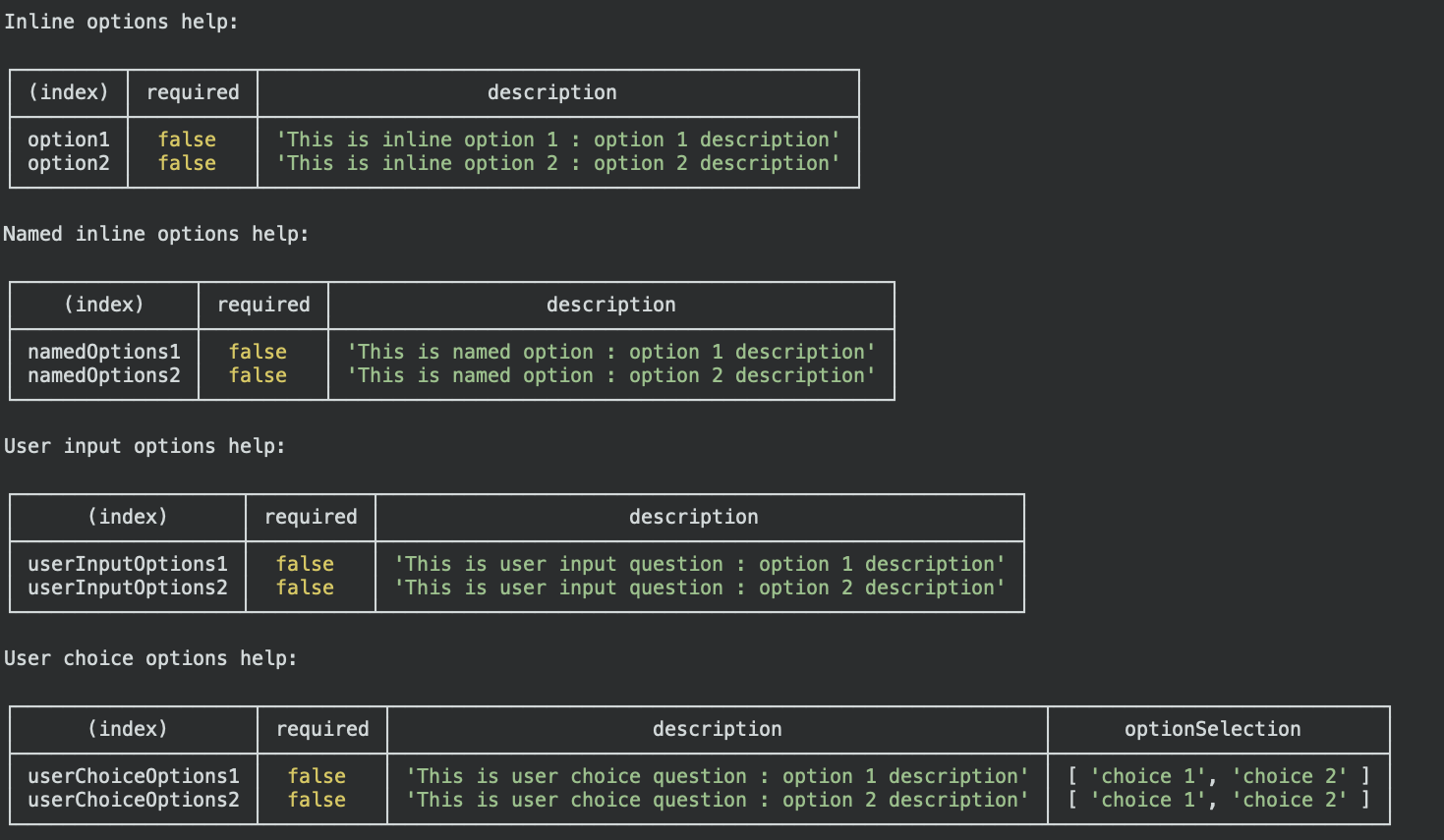
All options
a) Note if multiple type of options are needed, keys should be distinct, or else command parser will throw error. b) Follow below example for all inputs
// module
const VsCommandParser = require("@vs-org/command-parser").default;
// CJS
import VsCommandParser from "@vs-org/command-parser";
(async () => {
const commandParser = new VsCommandParser({
options: {
option1: {
description: "option 1 description"
},
option2: {
description: "option 2 description"
}
},
namedOptions: {
namedOptions1: {
description: "option 1 description"
},
namedOptions2: {
description: "option 2 description"
}
},
userInputOptions: {
userInputOptions1: {
question: "que 1?",
description: "option 1 description"
},
userInputOptions2: {
question: "que 2?",
description: "option 2 description"
}
},
userChoiceOptions: {
userChoiceOptions1: {
question: "que 1?",
choices: ["choice 1", "choice 2"],
description: "option 1 description"
},
userChoiceOptions2: {
question: "que 2?",
choices: ["choice 1", "choice 2"],
description: "option 2 description"
}
}
});
const ans = await commandParser.parse();
console.log(ans);
})();
Options
inline argument options
| option | required | Description | | --------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
description| false |String: description, will be used to show help | |transformer| false |Function: value transformer, if provided value processed through function and then returned. You can transform value after parsing as well | |validator| false |Function: Validation function to validate provided value against | |validationMsg| false |String: validation message to return if user provided value is not valid or not provided in case ofrequiredoption | |required| false |Boolean: flag for required validation |Named argument options
| option | required | Description | | --------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
description| false |String: description, will be used to show help | |transformer| false |Function: value transformer, if provided value processed through function and then returned. You can transform value after parsing as well | |validator| false |Function: validation function to validate provided value against | |validationMsg| false |String: validation message to return if user provided value is not valid or not provided in case ofrequiredoption | |required| false |Boolean: flag for required validation |User input argument options
| option | required | Description | | --------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
description| false |String: description, will be used to show help | |question| true |String: question which will be presented to user, if it is required then user will be presented question till user provides valid answer | |transformer| false |Function: value transformer, if provided value processed through function and then returned. You can transform value after parsing as well | |validator| false |Function: validation function to validate provided value against | |validationMsg| false |String: validation message to return if user provided value is not valid or not provided in case ofrequiredoption | |required| false |Boolean: flag for required validation |User choice argument options
| option | required | Description | | --------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
description| false |String: description, will be used to show help | |question| true |String: question which will be presented to user | |choices| true |Array<String>: choices for user to choose from, by default first option will be selected when options are rendered | |transformer| false |Function: value transformer, if provided value processed through function and then returned. You can transform value after parsing as well | |validator| false |Function: validation function to validate provided value against | |validationMsg| false |String: validation message to return if user provided value is not valid or not provided in case ofrequiredoption | |required| false |Boolean: flag for required validation |
License
MIT (see LICENSE)
Note
This package is tested with each and combined options, but there may be some unexpected errors or responses. Don't use it for critical flows without proper testing.
