cb-loggy
v1.1.6
Published
A Leightweight NodeJS Logger
Readme
Loggy
v1.1.4
A simple NodeJS logger that print the message to the console and write the message to the log files. The module is created to support the Stater project.
Since the Loggy is a class, you can create new loggy instance as many as you want, with different options. For example, you can create new loggy and save the log files to the each folder on your modules.
Usage
Install the module using npm install --save cb-loggy, and then load the module. After loaded, the Loggy class will available on the global object.
require('cb-loggy');
var log = new Loggy(options);Options
print- Print the message to the console screen. Default:truewrite- Write the message to the log file. Default:falsedtime- Add date-time to the message. Default:falsesigns- Add log sign ([i], [!], [x]) to the message. Default:falsereads- Allow to read the error files as code reference. Default:trueindent- Set the indent size. Default:4cwd- The folder path to write the log files in. Default:process.cwd()/logs
If you set the print option to false, but you define --verbose on the CLI command, the print option will be set to true.
Every message argument support indent pattern. So, if you want to indent the logs, you can simply add %LEVEL% pattern at beginning.
Example: loggy.info('%2% Indent level 2');.
If you set the write option to true, the log files will be written to the cwd path. Each log type will be written to the difference files, with info-, wanring-, and error- as the filename prefix, followed by current year-month-date.
Example: logs/info-2016-1-10.log
Example
require('cb-loggy');
// Configure the logger.
var loggy = new Loggy({
print : true, // Print the logs to the screen.
write : true, // Write the logs to the file.
signs : true, // Add signs to the logs.
dtime : true, // Add date-time to the logs.
reads : true // Read the files for error reference.
});
// Wrapping colors from loggy.
var grn = loggy.color.green,
ylw = loggy.color.yellow,
red = loggy.color.red;
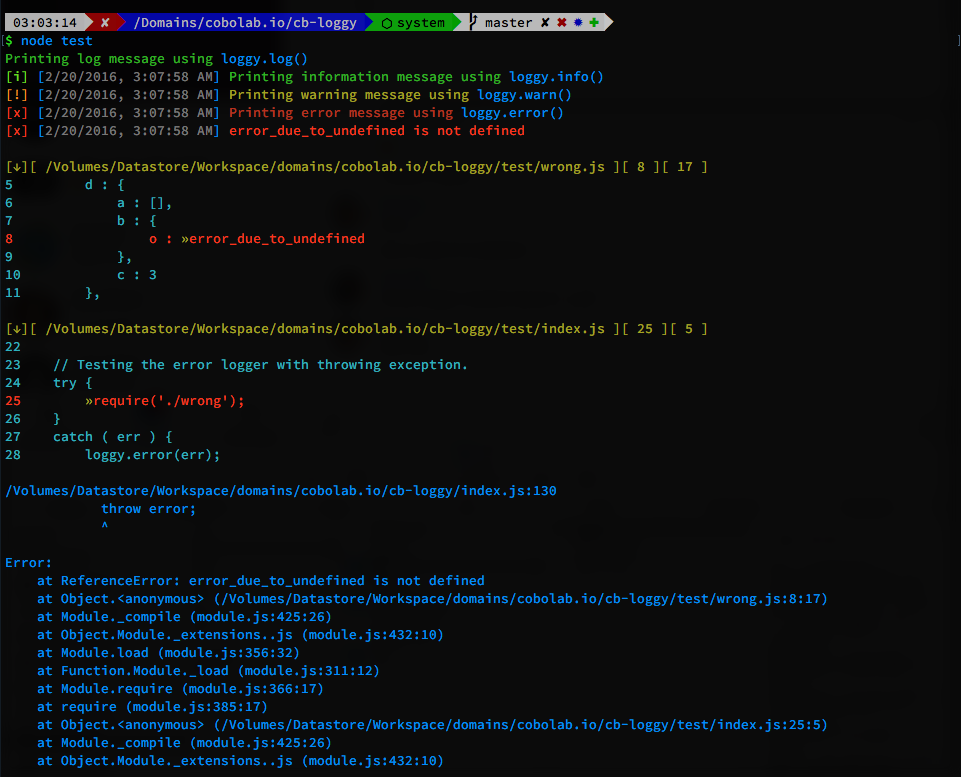
// Testing general logger, without breaking the runtime.
loggy.log(grn('Printing log message using ') + 'loggy.log()');
loggy.info(grn('Printing information message using ') + 'loggy.info()');
loggy.warn(ylw('Printing warning message using ') + 'loggy.warn()');
loggy.error(red('Printing error message using ') + 'loggy.error()');
// Testing the error logger with throwing exception.
try {
require('./wrong');
}
catch ( err ) {
loggy.error(err);
}
loggy.log()
Standar logger, act like console.log but with ability to save the logs.
Usage
loggy.log(message);message- [REQUIRED] - String message, can contains colorized strings.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
loggy.log('Standard log message.');loggy.info()
Information logger, will add [i] prefix to the logs message when the config is enabled.
Usage
loggy.info(message);message- [REQUIRED] - String message, can contains colorized strings.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
loggy.info(loggy.color.red('Information message.'));loggy.success()
Success logger, will add [√] prefix to the logs message when the config is enabled.
Usage
loggy.success(message);message- [REQUIRED] - String message, can contains colorized strings.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
loggy.success(loggy.color.red('Success message.'));loggy.warn()
Warning logger.
Usage
loggy.warn(message);message- [REQUIRED] - String message, can contains colorized strings.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
loggy.warn('Warning message');loggy.error()
Error logger, log the error message, or log the Error object and parse the error stack, including reading the files for reference.
Usage
loggy.error(info, skipCalls, sipFiles, slice);info- [REQUIRED] - String message and can contains colorized strings, or javascriptErrorobject. Using error object as info will makes the logger throwing exception.skipCalls- [OPTIONAL] - Array to exclude the function call name (e.g:Module.require) when parsing the error stack.skipFiles- [OPTIONAL] - Array to exclude the file name when parsing the error stack.slice- [OPTIONAL] - Number to slice the error stack.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
// Simply log the error without throwing exception.
loggy.error('Error message');
// Log the error with reading the files for reference, and then trhow the exception.
try {
require('undefinedmodule');
} catch(err) {
loggy.error(err);
}loggy.wait()
Display logs that wait some process by adding spinner on the beginning of the log message.
Usage
loggy.wait(message);message- [REQUIRED] - String message, can contains colorized strings.@return-{ done(), fail(ERROR_OBJECT) }return functions to mark the spinner as done or failed.
Example
const loggy = new Loggy();
let spin = loggy.wait('Fetching data from server');
setTimeout(function() {
spin.done();
// or
spin.fail(new Error());
});loggy.write()
Write message to the log file.
Usage
loggy.write(type, message);type- String log type, as the file name prefix. E.g:info.message- String message, can contains colorized strings.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
loggy.write('info', 'Some custom information');loggy.assert()
Check variable or argument, and throw exception when unsatisfied.
Usage
loggy.assert(what, then);what- [REQUIRED] - Variable or argument to test.then- [REQUIRED] - String error message, or function to handle the error. Using string will throw exception directly, and using function will not throw an exception but forward the error and stack to the handler. Handler will get(stack, error)arguments.
Example
var log = new Loggy();
// Function that contains the assert fill excluded from the error stack.
function fileReader(file) {
log.assert(isString(file), 'Argument ${log.color.green("file")} is required and must be string to call the "fileReader(file)."');
console.log('Continue if all fine');
}
// Part of error stack.
function indirectRead(file) {
return fileReader(file);
}
// Part of error stack.
function init() {
var content = indirectRead(); // Causing error since the arg is required.
console.log(content);
}
// part of error stack.
init();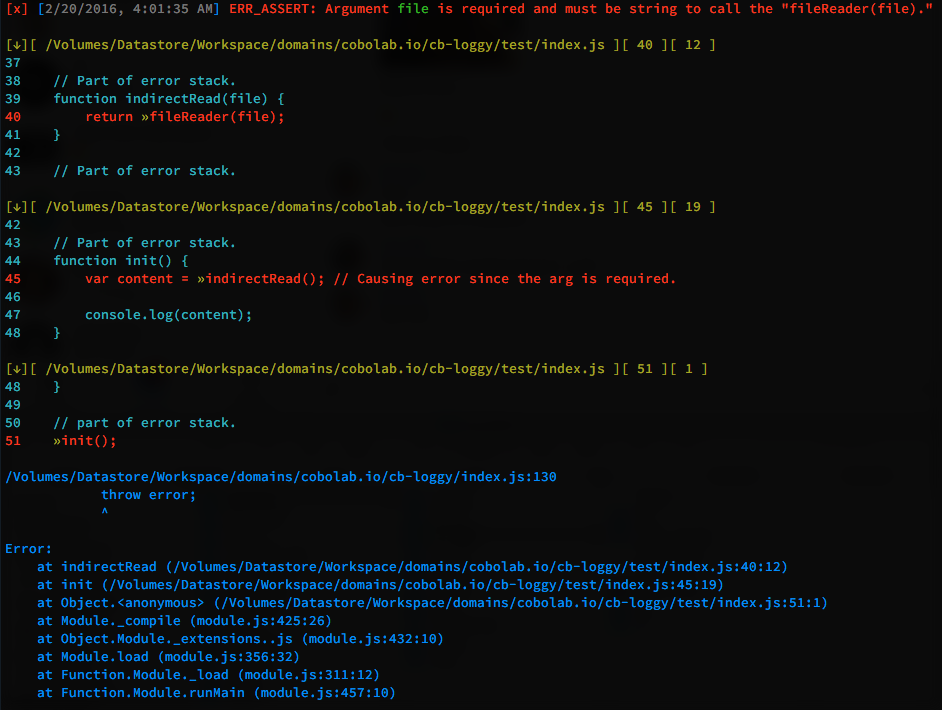
loggy.color
A CLI Color object to colorize the strings. For more informations, read the CLI Color Docs.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
loggy.log(loggy.color.bold('Bolded message'));loggy._cleanColor()
Remove the CLI colors from string.
Usage
loggy._cleanColor(text);text- String to clean the colors from.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
// Add color to string.
var msg = loggy.color.redBright('Colorized string.');
// Remove color from string.
var cln = loggy._cleanColor(msg);loggy._parseError()
Parse the error stack and read the stack files for reference.
Usage
loggy._parseError(error, skipCall, skipFile);error- [REQUIRED] - A javascript Error object to parse from.skipCall- [OPTIONAL] - Exclude stack function name from the stacks.skipFile- [OPTIONAL] - Exclude file from the stack.
RESULT
This function will return an Array contains stack infos. Each stack info will contains:
call- Stack function name.file- Stack file name.linerow- Stack line number on the file.col- Stack column number on the file.
text- Stack text contains readed code reference from the file.rawscurnline- Error line number.text- Error text.
list[]line- Code line number.text- Code text.
Example
var loggy = new Loggy();
// This function will be excluded from the stack, since the function name is added to the skipCall list.
function parseError() {
var err = new Error();
var stack = loggy._parseError(err, [ 'parseError' ]);
console.log(stack.text);
}
// This function will be added to the stack.
function otherStack() {
parseError();
}
// This function will be added to the stack.
otherStack();Changelog
v1.1.6 - Jun 05, 2016
- Fixing error with
'use strict';
v1.1.5 - May 10, 2016
- Makes the
.log()accept indentation.
v1.1.4 - May 1, 2016
- Move the waiting indicator to the end of lines.
- Added indent pattern (
%LEVEL%) to indent log messages. - Improvements.
v1.1.3 - May 1, 2016
- Fixing blank wait message when
dtimeoptions is undefined.
v1.1.2 - May 1, 2016
- Added
loggy.wait()method. - Added
JSCSconfig. - Added minimum NodeJS
v.5.6 - Fixing private configs.
- Prevent
Loggyregistered twice.
v1.1.1 - Mar 20, 2016
- Added
loggy.success()method. - Improved logger styles.
v1.1.0 - Feb 20, 2016
- Changed
loggy.log()to act likeconsole.log. - Added
loggy.info()to log an information logs. - Added
loggy.assert() - Added
loggy._parseError() - Added
loggy._cleanColor() - Imrpovement of
loggy.error()
