ds-algorithms
v1.0.4
Published
Data Sturctures package for javascript that adds new data structures and improves existing ones
Downloads
2
Maintainers
Readme
DS - Algorithms
An npm package that adds new data structures and improves existing ones.
Installation
npm i ds-algorithms --save
Usage
const dataStructures = require("ds-algorithms");
let SlinkedList = new dataStructures.SinglyLinkedList();
let DlinkedList = new dataStructures.DoublyLinkedList();
let stack = new dataStructures.Stack();
let queue = new dataStructures.Queue();
SlinkedList.add(3);
SlinkedList.add(7);
DlinkedList.add(2);
DlinkedList.add(5);
stack.push(4);
stack.pop();
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.dequeue();Options
Singly Linked List
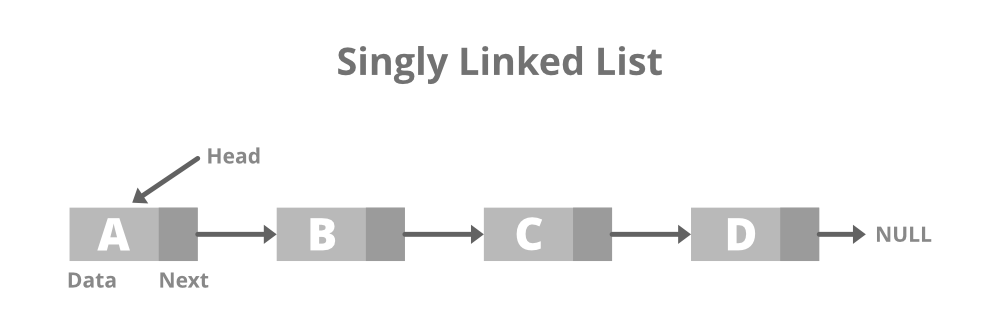
In a singly linked list data is stored in individual objects named nodes. Each node has a value and link to the next node. The main advantage of using a linked list over an array is that we generally could add and delete data much faster and is stored at discontinuous locations in memory. A singly linked list is slightly limited in functionality than the doubly linked list but is generally faster than singly linked list.
Methods:
add(value) - adds a value to the end of the linked list
prepend(value) - adds a value to the start of the linked list
insertAt(index, value) - adds a value to the node at index + 1 position in the linked list i.e. if index is 0 the value is added at the 1st node in the list
removeFrom(index) - removes the node at index + 1 position in the linked list, returns the deleted value
removeValue(value) - removes the first node which has the same value, returns the deleted value
indexOf(value) - returns the index of the given value
isEmpty() - returns true if the list is empty
toArray() - returns the linked list as an array
display() - prints the graphical representation of the linked list in the console
forEach(callback) - calls the callback function for each element in the list and passes the value of each node as an argument to the callback function
clearAll() - clears the list
Doubly Linked Lists
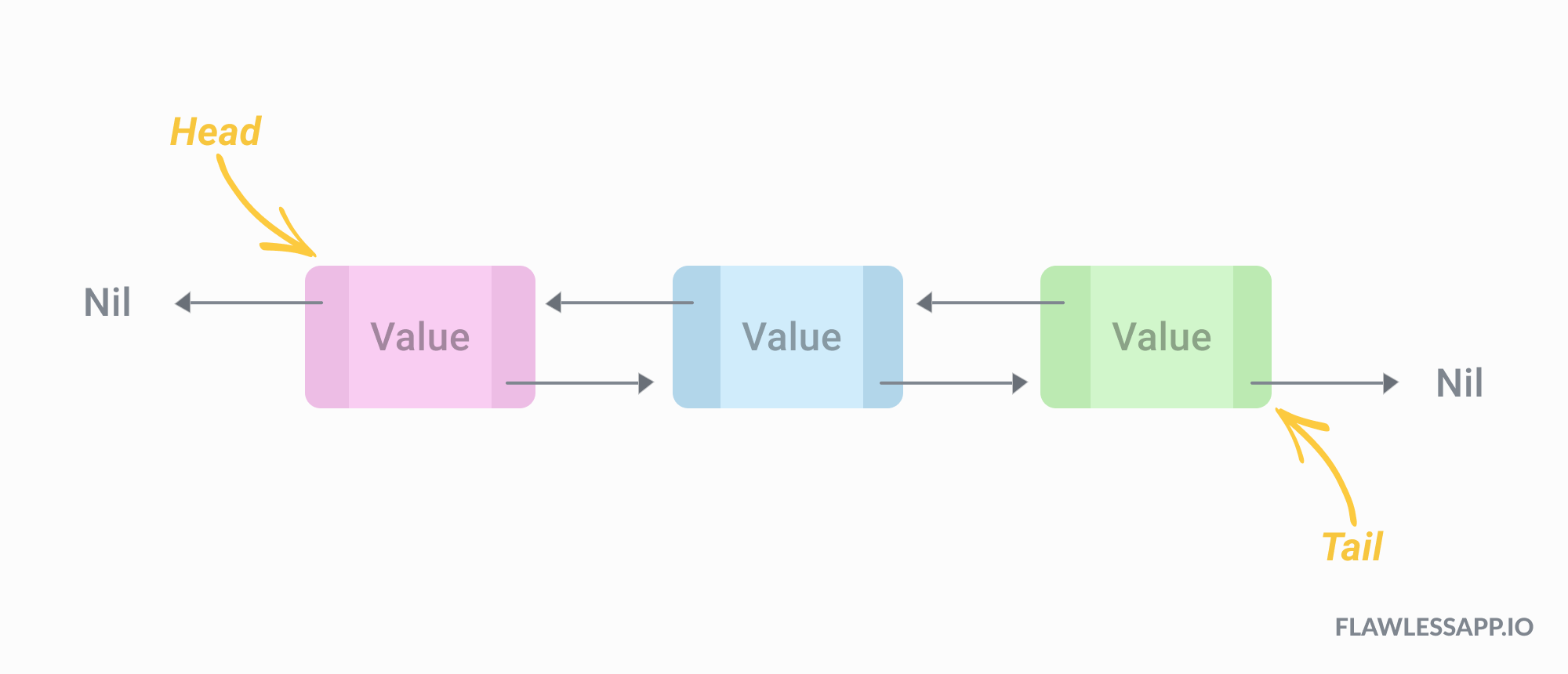
In a doubly linked list data is stored in individual objects named nodes. Each node has a value and link to the next node and a link to the previous. The main advantage of using a linked list over an singly linked list is that its much more useful but slightly slower.
Methods:
add(value) - adds a value to the end of the linked list
prepend(value) - adds a value to the start of the linked list
insertAt(index, value) - adds a value to the node at index + 1 position in the linked list i.e. if index is 0 the value is added at the 1st node in the list
removeFrom(index) - removes the node at index + 1 position in the linked list, returns the deleted value
removeValue(value) - removes the first node which has the same value, returns the deleted value
indexOf(value) - returns the index of the given value
isEmpty() - returns true if the list is empty
toArray() - returns the linked list as an array
display() - prints the graphical representation of the linked list in the console
forEach(callback) - calls the callback function for each element in the list and passes the value of each node as an argument to the callback function
clearAll() - clears the list
Stack
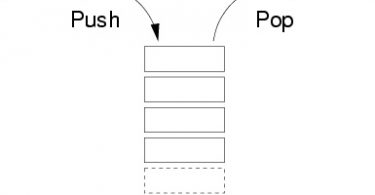
A stack is a collection of items in which only the most recently added item may be removed first. The latest added item is at the top. It is commonly used for implementing undo features, call stacks etc.
Methods:
push(value) - adds a value to the top of the stack
pop() - removes a value from the top of the stack, returns the deleted value
peek() - returns the value at the top of the stack without removing it
indexOf(value) - returns the index of the given value
isEmpty() - returns true if the stack is empty
toArray() - returns the stack as an array
display() - prints the graphical representation of the stack in the console
clearAll() - clears the list
Queue
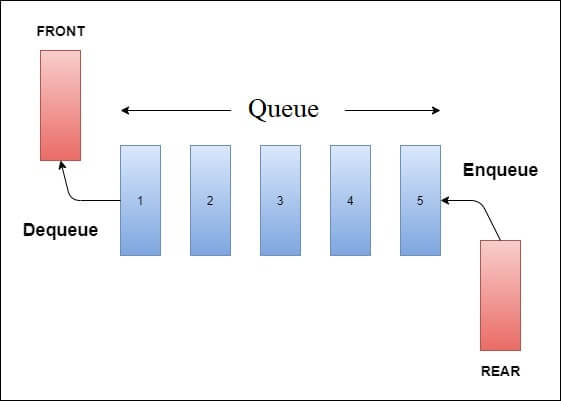
A queue is a collection of items in which only the earliest added item may be accessed first. Basic applications of queue include priority queue or serving shared resources to a single server etc.
Methods:
enqueue(value) - adds a value to the first position of the queue
dequeue() - removes a value from the first position of the queue, returns the deleted value
first() - returns the value from the first position of the queue without removing it
isEmpty() - returns true if the stack is empty
display() - prints the graphical representation of the stack in the console
clearAll() - clears the list
