immutable-tree-module
v1.0.12
Published
Immutable, fully persistent, and balanced binary search tree data structure implementation in pure js.
Maintainers
Readme
Immutable Tree
Immutable, fully persistent, and balanced binary search tree data structure implementation in pure js.
- Can run in browser and nodejs environments.
- Can be used in js, ts and rescript projects.
Tests available! Time complexity for insertion, deletion and search is O(log n) since this is an implementation of Red Black Tree. Try it here.
Installation
- For JS and TS projects
npm i immutable-tree-module --save
- For Rescript project
npm i immutable-tree-module --save- Update bs-dependencies in bsconfig.json
"bs-dependencies": ["immutable-tree-module"]- Ensure you clean build your rescript project
Usage in JS
import { fromArray, ImmutableTree } from "immutable-tree-module";
const compare = (a, b) => a - b;
// Create tree
new ImmutableTree(compare);
// Create from array of values
fromArray(compare, [1, 2, 3]);
// Chainable
new ImmutableTree(compare)
.insert(1)
.insert(2)
.insert(3)
.insert(6)
.deleteNode(2)
.printTreeAsc(); // Print in ascending orderUsage in TS
import { fromArray, ImmutableTree } from "immutable-tree-module";
const compare = (a: number, b: number) => a - b;
// Create tree
new ImmutableTree<number>(compare);
// Create from array of values
fromArray<number>(compare, [1, 2, 3]);
// Chainable
new ImmutableTree<number>(compare)
.insert(1)
.insert(2)
.insert(3)
.insert(6)
.deleteNode(2)
.printTreeAsc(); // Print in ascending orderUsage in Rescript
module FloatTree = ImmutableTree.Make({
type t = float
let compare = compare
})
FloatTree.empty()
->FloatTree.insert(1.)
->FloatTree.insert(2.)
->FloatTree.insert(3.)
->FloatTree.insert(6.)
->FloatTree.deleteNode(2.)
->FloatTree.printTreeAsc
open FloatTree
fromArray([10., 20., 30., 40.])->printTreeDescAPI :
insert:
Insert element into the tree
search:
Search for an element
searchWithDefault:
A convenient alternate for search. Default value provided will be returned if no element was found. Check tests for usage.
searchRange:
Search for all the elements in a particular range. Check tests for usage.
deleteNode:
Delete node from tree
update:
Update an element based on the provided compare function
printTreeAsc:
Prints the data in the tree in ascending order
printTreeDesc:
Prints the data in the tree in descending order
getMin:
Get the minimum value from the tree
getMax:
Get the maximum value from the tree
fromArray:
Create tree from a given array
toArray:
Convert to array from tree
traverseInOrder:
Does In Order Traversal on the tree . Check tests for usage.
traversePreOrder:
Does Pre Order Traversal on the tree . Check tests for usage.
traversePostOrder:
Does Post Order Traversal on the tree . Check tests for usage.
fold:
fold on values of the tree in ascending order. Similar to reduce function for arrays. Check tests for usage.
foldLeft:
An alias for the fold function. Check tests for usage.
foldRight:
fold on values of the tree in descending order. Check tests for usage.
empty:
Creates an empty node
getLeft:
Gets left tree of current tree node. This can be used to perform raw iteration over the tree. Check tests for usage.
getRight:
Gets right tree of current tree node. This can be used to perform raw iteration over the tree. Check tests for usage.
getHeight:
Gets height or depth of the current tree. Check tests for usage.
getLength:
Gets length or total number of elements in the tree. An empty tree returns 0. Check tests for usage.
isEmpty:
Returns true if the tree is empty else false.
How does Immutable Tree work?
Immutable tree is a fully persistent, balanced, functional binary search tree data structure. It is an immutable Red Black Tree. This means, tree is never modified or updated during any operation. Only a new tree is created with nodes either added or removed.
Well, then is it cloning the entire tree? That must be consuming high memory right? The answer is, No. Immutable Tree, optimally reuses the untouched nodes and creates new nodes necessary only for the path accessed by the current operation. Lets see an example.
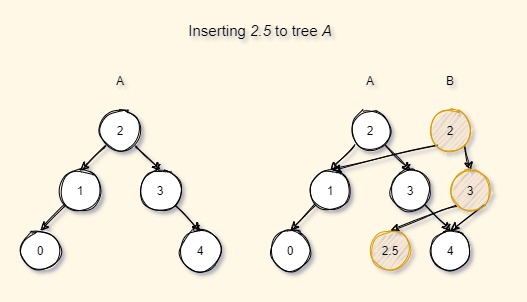
Insertion :
Check the below image. Consider that we want to insert a new value 2.5 to the tree A. Tree A is not directly modified or updated but a new series of nodes are created while traversing from the root to the node where the insertion has happened while still reusing the existing nodes (here node 1 and all its children).
Deletion :
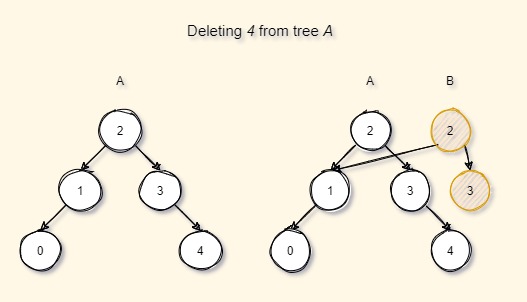
Consider that we want to delete a value 4 from the tree A. Tree A is not directly modified or updated but again a new series of nodes are created while traversing from the root to the node that has to be deleted, while still reusing the existing nodes (here node 1 and all its children).
Why Immutable Tree?
Well it has all benefits as any other immutable data structure.
- Easy to reason about the code and maintain
- Can be reused with out the fear of modification
- Time travelling
- Write pure, side effect free functions
Issues
Found issue? Please report it here.
Note :
Internal representation of the tree might not be readable. So for logging the tree, please use the in built functions like printTreeAsc or printTreeDesc.
