ma-dino-game
v0.3.1
Published
A simple, animated dino game.
Downloads
954
Readme
Dino Game
Simple Dino Game
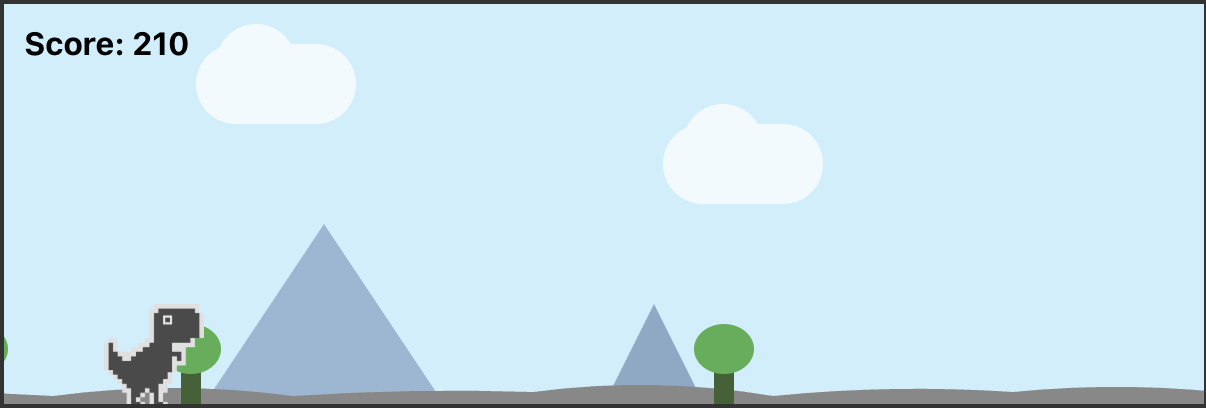
Installation
npm install ma-dino-game react react-domNote: This package requires react and react-dom as peer dependencies. Make sure they are installed in your project.
Usage
import DinoGame from 'ma-dino-game';
function App() {
return <DinoGame />;
}Note: The CSS is automatically injected, so no separate import is needed.
Next.js Support
This package is fully compatible with Next.js and Server-Side Rendering (SSR). The component will only render on the client side to avoid SSR issues.
For Next.js, use dynamic import:
import dynamic from 'next/dynamic';
const DinoGame = dynamic(() => import('ma-dino-game'), { ssr: false });
function App() {
return <DinoGame />;
}Troubleshooting
"Cannot read properties of null (reading 'useState')" Error
This error occurs when React cannot be resolved properly, typically due to module resolution conflicts.
Why does this happen?
This package correctly externalizes React (doesn't bundle it) so it can use your app's React instance. However, some bundlers (especially Next.js webpack) have trouble resolving the external React module from npm packages.
Solution for Next.js (RECOMMENDED):
Add this webpack alias configuration to your next.config.js or next.config.mjs:
const path = require('path'); // or import path from 'path' for .mjs
/** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */
const nextConfig = {
webpack: (config, { isServer }) => {
// Ensure React is resolved from the app's node_modules
if (!isServer) {
config.resolve.alias['react'] = path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/react');
config.resolve.alias['react-dom'] = path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/react-dom');
}
return config;
},
};
module.exports = nextConfig;For Next.js 13+ with ES modules (next.config.mjs):
import path from 'path';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
const __dirname = path.dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
/** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */
const nextConfig = {
webpack: (config, { isServer }) => {
if (!isServer) {
config.resolve.alias['react'] = path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/react');
config.resolve.alias['react-dom'] = path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/react-dom');
}
return config;
},
};
export default nextConfig;Alternative Solutions:
Follow these steps in your consuming application:
Install React as dependencies (not devDependencies):
npm install --save react react-domDelete node_modules and package-lock.json, then reinstall:
rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json npm installCheck for duplicate React instances:
npm ls reactIf you see multiple versions (UNMET PEER DEPENDENCY or multiple entries), add to your
package.json:"overrides": { "react": "^19.0.0", "react-dom": "^19.0.0" }Then run
npm installagain.For Next.js 14+:
- Clear the
.nextcache:rm -rf .next - Make sure you have
'use client'at the top of your page component - Use the dynamic import pattern shown above
- Clear the
Verify React is installed correctly:
node -e "console.log(require('react'))"This should print the React module object, not
nullorundefined.If using npm link or local development:
cd /path/to/ma-dino-game npm link cd /path/to/your-app npm link ma-dino-game npm install react react-dom
