mongodb-transaction
v0.5.4
Published
Distributed Transactional In-Memory Database
Maintainers
Readme
Performance and Scalable
- Fast in memory data access, up to 25,000 ops (single doc read/write) per shard (each shard take one CPU core).
- System capacity is horizontally scalable, performance grows linearly by adding more shards.
- No single point bottleneck, all part of system is scalable, unlimited capability potential.
True Distributed ACID Transaction
- True ACID(Stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transaction support on distributed environment.
- MemDB brings ACID transaction support for MongoDB, on distributed environment! You can get full transaction support of traditional SQL database (like MySQL), while not losing the scalability of NoSQL database (like MongoDB).
MongoDB and Mongoose Compatible
- It's just a 'MongoDB' with a cache layer which support distributed transaction.
- Directly use of MongoDB's query API.
- Built-in Mongoose support, easy to port existing Mongoose project to MemDB.
High Availability
- Each shard is backed by one or more slaves, no single point of failure.
Links
- Home Page: http://memdb.org
- Github: https://github.com/memdb/memdb
- Wiki : https://github.com/memdb/memdb/wiki
- Mailing list: [email protected]
- Email: [email protected]
Quick Start
Install Dependencies
Make sure Redis and MongoDB has started
Install MemDB
- MemDB should be installed globally
sudo npm install -g memdb-serverConfigure MemDB
Copy default config file from node_modules/memdb-server/memdb.conf.js to ~/.memdb/ (mkdir if not exist), and modify it on your need.
Please read comments carefully.
Start MemDB
Use memdbcluster to control lifecycle of memdb server cluster
memdbcluster [start | stop | status] [--conf=memdb.conf.js] [--shard=shardId]Play with memdb shell
See the video bellow, note how ACID transaction work cross multiple shards.

Mdbgoose
Mdbgoose is a modified Mongoose version that work for memdb
var memdb = require('memdb-client');
var P = memdb.Promise;
var mdbgoose = memdb.goose;
// Define player schema
var playerSchema = new mdbgoose.Schema({
_id : String,
name : String,
areaId : Number,
deviceType : Number,
deviceId : String,
items : [mdbgoose.SchemaTypes.Mixed],
}, {collection : 'player'});
// Define player model
var Player = mdbgoose.model('player', playerSchema);
var main = P.coroutine(function*(){
// Connect to memdb
yield mdbgoose.connectAsync({
shards : { // specify all shards here
s1 : {host : '127.0.0.1', port: 31017},
s2 : {host : '127.0.0.1', port: 31018},
}
});
// Make a transaction in s1
yield mdbgoose.transactionAsync(P.coroutine(function*(){
var player = new Player({
_id : 'p1',
name: 'rain',
areaId : 1,
deviceType : 1,
deviceId : 'id1',
items : [],
});
// insert a player
yield player.saveAsync();
// find player by id
var doc = yield Player.findByIdAsync('p1');
console.log('%j', doc);
// find player by areaId, return array of players
var docs = yield Player.findAsync({areaId : 1});
console.log('%j', docs);
// find player by deviceType and deviceId
player = yield Player.findOneAsync({deviceType : 1, deviceId : 'id1'});
// update player
player.areaId = 2;
yield player.saveAsync();
// remove the player
yield player.removeAsync();
}), 's1');
});
if (require.main === module) {
main().finally(process.exit);
}To run the sample above:
- Add the following index config in memdb.conf.js
collections : {
player : {
indexes : [
{
keys : ['areaId'],
},
{
keys : ['deviceType', 'deviceId'],
unique : true,
},
]
}
}- restart memdb cluster
memdbcluster stop
memdbcluster start- Make sure you have started shard 's1' on localhost:31017
- Install npm dependencies
npm install memdb-client- Run with node >= 0.12 with --harmony option
node --harmony sample.jsCheck here to see how to port your Mongoose project to Mdbgoose
Architecture
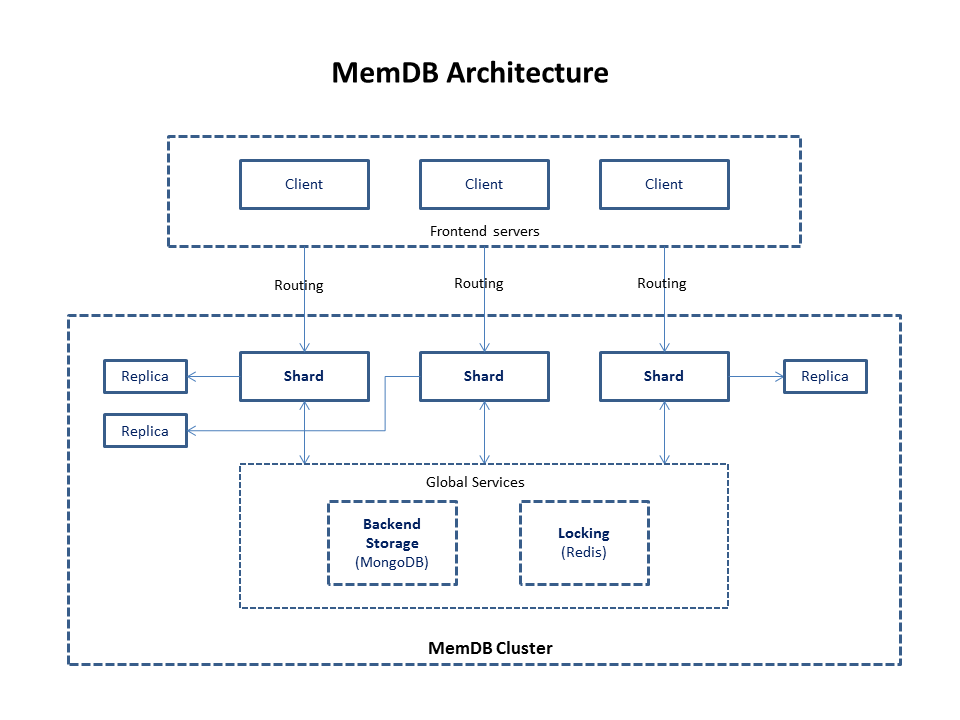
Relationship between MemDB and MongoDB
MemDB is like a 'cache layer' built up on MongoDB which support distributed ACID transaction.
MemDB has its own API which similar to MongoDB, however, you can still use MongoDB's native query API by directly access backend storage, here are the guidelines:
- Do simple query and update through MemDB API, which is ACID transaction safe.
- Do complex query through backend MongoDB, the read is not transaction safe.
- Do complex update through backend MongoDB offline (All MemDB shards are shutdown).
Here are some basic rules for memdb:
- Data is not bind to specified shard, you can access any data from any shard.
- All operations inside a single transaction must be executed on one single shard.
- Access the same data from the same shard if possible, which will maximize performance.
Further read
License
Copyright 2015 The MemDB Authors.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. See the AUTHORS file for names of contributors.
