regression
v2.0.1
Published
Javascript least squares data fitting methods
Maintainers
Readme
Installation
This module works on node and in the browser. It is available as the 'regression' package on npm. It is also available on a CDN.
npm
npm install --save regressionUsage
import regression from 'regression';
const result = regression.linear([[0, 1], [32, 67], [12, 79]]);
const gradient = result.equation[0];
const yIntercept = result.equation[1];Data is passed into the model as an array. A second parameter can be used to configure the model. The configuration parameter is optional. null values are ignored. The precision option will set the number of significant figures the output is rounded to.
Configuration options
Below are the default values for the configuration parameter.
{
order: 2,
precision: 2,
}Properties
equation: an array containing the coefficients of the equationstring: A string representation of the equationpoints: an array containing the predicted data in the domain of the inputr2: the coefficient of determination (R2)predict(x): This function will return the predicted value
API
regression.linear(data[, options])
Fits the input data to a straight line with the equation 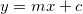 . It returns the coefficients in the form
. It returns the coefficients in the form [m, c].
regression.exponential(data[, options])
Fits the input data to a exponential curve with the equation 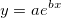 . It returns the coefficients in the form
. It returns the coefficients in the form [a, b].
regression.logarithmic(data[, options])
Fits the input data to a logarithmic curve with the equation 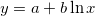 . It returns the coefficients in the form
. It returns the coefficients in the form [a, b].
regression.power(data[, options])
Fits the input data to a power law curve with the equation 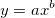 . It returns the coefficients in the form
. It returns the coefficients in the form [a, b].
regression.polynomial(data[, options])
Fits the input data to a polynomial curve with the equation 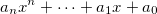 . It returns the coefficients in the form
. It returns the coefficients in the form [an..., a1, a0]. The order can be configure with the order option.
Example
const data = [[0,1],[32, 67] .... [12, 79]];
const result = regression.polynomial(data, { order: 3 });Development
- Install the dependencies with
npm install - To build the assets in the
distdirectory, usenpm run build - You can run the tests with:
npm run test.
